The doctors of the clinic "Quality of Life" will help to quickly and effectively remove swelling. A specialist will listen to complaints, asking for pain and their character.
How to get rid of edema
Adult man by 66-75% consists of water. Of these, about 2/3 is in cells, and another third – in the intercellular space. Evenum appears with an increase in the amount of fluid in the intercellular matrix. The reasons for this may be a huge amount – from injuries of fabrics and bruises, to abundant drinking, salt or alcohol. Enevelops are a cluster of blood plasma from lymphatic and blood vessels. These violations may be the result of overheating, deterioration of blood supply, the actions of some drugs, problems with heart, kidney or other bodies. Often they are caused by a violation of lymphatic drainage, when the rate of fluid outflow from tissues is reduced. Lymphatic vessels have their own valves and even a musculature that regulates the outflow of lymphs. However, with age, in the case of poor heredity or at strong loads, they do not cope with their tasks.
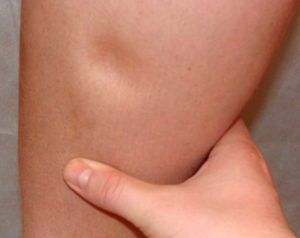
Edema – swelling of soft tissues as a result of an increase in the volume of interstitial fluid. This liquid consists mainly of water, but may also contain amino acids and cells (with infections or obstruction of lymphatic vessels).
Liquid can have a different composition and consistency. This is:
• transudate – poor protein (less than 2%) liquid;
• Exudate is rich in protein (over 3%, sometimes up to 7-8%) liquid, which often contains blood shaped blood elements;
• mucus – a mixture of water and colloids with hyaluronic and chondroitrine acid (develops with myxedema).
Liquid accumulation can be generalized or local (for example, on one limb or part). Sometimes it arises suddenly, the patient begins to complain to an increase in the volume of one hand or legs. Often swelling develop gradually, begin with weight gain, swelling in the morning. Slowly developing fluid accumulations can become very massive before the patient appeals for help.
How to get rid of?
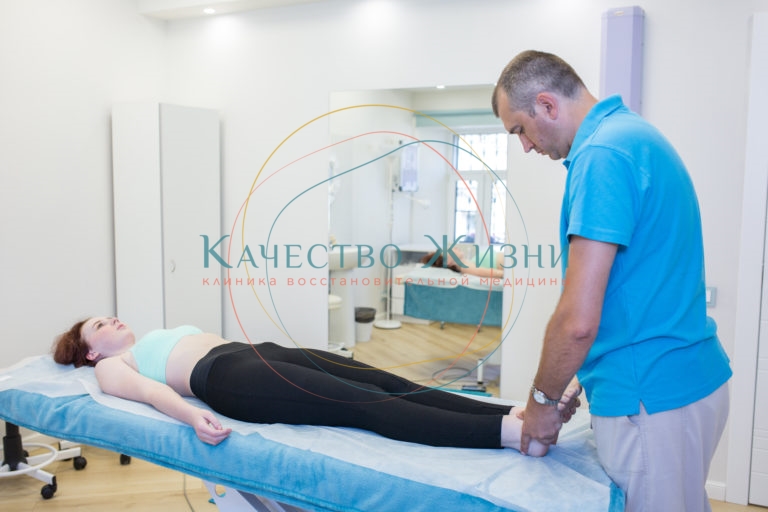
The doctors of the clinic "Quality of Life" will help quickly and effectively remove the cluster of the fluid. During the diagnosis, the specialist carefully listens to the complaints, asking for pain, the nature of pain, strengthening time. At the reception is important to report on the presence of injuries, bruises, transferred surgical interventions. Experienced clinic doctors take into account the results of instrumental research, laboratory and functional diagnostics – all this will help to understand the picture of the disease and evaluate its development in dynamics.
During the examination, the doctor assesses the elasticity and mobility of the joints. Manual muscle testing is the base of the kinesiology.The method is aimed at testing the reaction of muscles during movement. It allows the specialist to direct the diagnosis in the right direction.
In the arsenal of the doctors of the clinic are not only diagnostic, but also corrective techniques, manual therapy and kinesiology:
• structural is aimed at working with the spine, joints and muscular system;
• visceral – to work with internal organs;
• cranial – normalizes the micro-mobility of bones and structures of the spine to normalize blood circulation and circulation of cerebrospinal fluid.
Our doctors treat the body, not the symptom. In some cases, the accumulation of fluid disappears after the bones of the skull, organs, vertebrae and joints return to the anatomically correct position. This leads to the strengthening of the immune and genitourinary systems, the musculoskeletal system, the heart and blood vessels.
Additionally, massage, physiotherapy exercises, kinesio taping can be prescribed. With varicose veins, the patient may be advised to wear medical compression stockings. In combination with therapeutic physical culture, knitwear activates the venous-muscular pump, the valves of the veins begin to close better, and the blood moves more efficiently to the heart. Compression clothing relieves the symptoms of vascular disease and improves the quality of life with varicose veins.
Lymphatic drainage can be prescribed both as a separate physiotherapeutic manipulation and as part of a complex rehabilitation. After the completed course, lymph outflow is restored, tissue metabolism improves, and fluid accumulation is eliminated. As a result, the patient can get rid of a few extra pounds. Depending on the indications of the doctor, different techniques can be selected – the effectiveness of each method depends on the individual characteristics of the patient.
Osteopathic medicine, combining the principles of neurology, biomechanics, orthopedics, manual therapy and neurophysiology, is an effective method. Osteopathic correction is not aimed at temporary relief of symptoms, but at complete healing.
Types and causes
Violation can manifest itself in various signs, depending on the causes:
• With an increase in hydrostatic pressure and heart failure, swelling is often symmetrical and depends on the position of the body. These signs are often combined with shortness of breath during exercise, orthopnea.
• Certain medications (eg, minoxidil, NSAIDs, estrogens, fludrocortisone, dihydropyridines, diltiazem, other calcium channel blockers) often cause fluid retention. It is painless and depends on the position of the body.
• With venous obstruction, acute, mild swelling is observed, usually on one leg.
• With deep vein thrombosis, one or two legs are chronically swollen, brown skin pigmentation, and discomfort are observed.Сильные боли не характерны, но иногда возможны язвенные поражения кожных покровов.
• Наружная компрессия вен может приводить к полнокровию лица, увеличению шейных вен и задержке жидкости ног. Такое часто случается при длительном постельном режиме или длительном пребывании в одном положении (например, во время перелета).
• При ангиоэдеме (отек Квинке) отечность появляется внезапно и не зависит от положения тела.
Отеки могут быть истинными или ложными. Ложные часто сопровождают ожирение, системную склеродермию и миксидему. Они имеют характерную особенность: при надавливании пальцем на кожу ямки не остается. При истинном ямка не пропадает в течение длительного времени, что свидетельствует о свободном перемещении воды в межклеточном пространстве. Однако и здесь есть ряд исключений.
Отекание возникает в результате изменения биохимического состава крови и тканевой жидкости, гормональных нарушений, повышения проницаемости капиллярных стенок, затруднения оттока венозной крови и лимфы, нарушения газообмена или выделительной функции почек. Кроме того, задержка жидкости нередко возникает в результате застойных явлений при сердечной недостаточности, критической ишемии или малоподвижного образа жизни.
Истинные отеки делятся на локальные и общие. При общих жидкость скапливается во всем организме, при локальных – только на одном участке. Каждый из этих двух типов может иметь много разновидностей. Мы лечим все виды нарушений
General
• Легочная или сердечная недостаточность. Сила тяжести приводит к скоплению жидкости в самых низкорасположенных частях тела. У лежачих пациентов это крестец и поясница. Нарушение сопровождается одышкой, набуханием вен шеи, застойными печеночными явлениями, асцитом, гидротораксом и другими характерными признаками.
• Заболевания почек — гломерулонефрит, пиелонефрит, почечная недостаточность и другие патологии. Жидкость сначала скапливается на лице (как правило, на веках), а потом переходит на конечности и туловище. С развитием нефротического синдрома возможно распространение по всему телу, в том числе в серозные полости. В таких случаях говорят об отечном синдроме.
• Cirrhosis of the liver. Помимо скопления жидкости, болезнь проявляется асцитом, расширением вен пищевода, пищеводными кровотечениям, печеночной недостаточностью.
• Истощение. Скопление жидкости может быть вызвано голоданием, алкоголизмом и некоторыми заболеваниями ЖКТ, при которых наблюдается ускоренное выведение протеина из организма. При истощении отекают стопы и голени, а также лицо.
Местные отеки
• Варикозное расширение вен ног. Зачастую отекает нижняя треть голени (с двух сторон или несимметрично, с преобладанием задержки жидкости на одной стороне). Это происходит после продолжительного стояния на ногах и проходит после того, как человек ляжет и приподнимет ноги.
• Тромбоз и тромбофлебит подкожных вен. The extremities may swell as a result of blockage of the veins by blood clots. This often occurs after childbirth, surgical interventions on the digestive tract, with tumor processes, leukemia and some other pathologies. In acute thrombosis and thrombophlebitis, the phenomenon is usually unilateral, occurs suddenly, growing and becoming permanent. There is a characteristic soreness. Thrombophlebitis is accompanied by local seals and hyperemia of the extremities along the affected vessel.
• Post-thrombophlebitic syndrome. Fluid retention is most often unilateral and may extend to both the leg and thigh. After 2-3 years, these manifestations can be joined by varicose veins, pigmentation, thickening of fatty tissue under the skin and trophic changes in the skin – ulcers, dermatitis.
• Lymphedema. With them, the foot and lower leg begin to swell, and in the last stages of the disease, the thigh. Most often, the lesion is unilateral. In the initial stages, the fluid is retained only temporarily, but then it happens permanently. In advanced cases, edema can be very dense, fibrous growths can occur on the feet and knees. Recurrent erysipelas, malignant neoplasms of the intestine and pelvic organs, and infectious lesions of the lymph nodes in the groin can act as a triggering factor. The combination of lymphedema with varicose veins is called phlebolymphedema. Fluid retention in such cases is most often bilateral, sometimes trophic ulcers are possible.
• Pathology of the brain. Tumors, encephalitis and other diseases of the central nervous system, which are accompanied by paralysis of the limbs, can cause the accumulation of fluid on the side of the paralysis. This is due to a decrease in the contractility of the muscles and paresis of the lymphatic vessels.
• Injuries. There is a rupture of small blood vessels, which leads to a hematoma. The affected areas swell. Especially dangerous fluid retention in the brain in traumatic brain injury.
• Obliterating endarteritis. This is a chronic vascular disease that affects mainly the arteries of the lower extremities.
In addition, idiopathic puffiness is distinguished – their causes cannot be established.
You should definitely consult a specialist if the violations are accompanied by severe pain, shortness of breath, hemoptysis, painful sensitivity. A sudden appearance is also a reason to visit a doctor.
How to relieve pain
Traditional medicine treats excess fluid accumulation depending on the cause of its development. Treatment regimens often include
• limiting fluid intake;
• reduction of salt and sodium in general;
• taking diuretics.
All of them have a lot of side effects. Diuretics, for example, can reduce the amount of potassium, which negatively affects the work of the heart and further exacerbates the problem.
Osteopathic medicine looks at a different way. The human body is anatomically and functionally interrelated system. The fascial fabric that covers all the muscles, a ligament and nerves, provides a clear anatomical connection. This connection works at all levels of organ interaction. An example of such a connection is the "transmission" of the spasm of the diaphragm to the liver, stomach or intestines, which is manifested by colic or constipation.
One of the principles of osteopathic medicine is that the structure manages the function, and vice versa. It becomes more understandable if we consider the displacement of the vertebrae or organs. The displaced vertebra (structure) violates the functions of nearby and remote departments, leads to excessive mobility and protective spasming of muscles to eliminate it. There are high risks that muscle spasm will surrend the veins and fabrics around the vertebrae, as a result of which the liquid begins to accumulate.
Osteopaths believe that the CNS underlies integration. The central nervous system suffers from the impaired blood flow, the outflow of lymph and the movement of the cranial box bones. These problems violate the functionality of the whole body.
Osteopathic medicine treats the body as a whole. The task of a specialist is to eliminate the arisers and displacements to activate self-healing resources.