<h3>ЦЕЛЬ ИССЛЕДОВАНИЯ</h3><p>Изучение клинической эффективности растительного комплекса «НефроБест», зарегистрированного как биологически активная добавка, для оптимизации терапии беременных с бессимптомной бактериурией (ББ).</p><h3>МАТЕРИАЛ И МЕТОДЫ</h3><p>Проведено обследование и лечение 52 беременных с бессимптомной бактериурией. Обследование включало бактериоскопическое исследование мазка на микрофлору, молекулярно-биологическое исследование вагинального содержимого (тест «Фемофлор») и мочи (бактериологическое исследование, общий анализ мочи), УЗИ почек. Исследование комплаенса терапии осуществлялось посредством анкетирования пациенток. В 1-й группе (<i>n</i>=32) наряду с антибактериальной терапией назначался препарат «НефроБест» по 1 капсуле 2 раза в день, до 3 мес, во 2-й группе (<i>n</i>=20) наряду с антибактериальной терапией назначался канефрон Н по 2 таблетки 3 раза в день, до 3 мес.</p><h3>РЕЗУЛЬТАТЫ</h3><p>Выявлено, что использование способа комбинированного лечения беременных с ББ с применением на фоне антибактериальной терапии растительного комплекса отечественного производства «НефроБест» в течение 3 мес привело к стойкой ремиссии и отсутствию рецидивирования.</p><h3>ЗАКЛЮЧЕНИЕ</h3><p>Выявленные положительные корреляционные связи ББ с бактериальным вагинозом (<i>r</i>=+0,743 при <i>p</i>=0,001) диктуют необходимость включения обследования репродуктивного тракта и лечения пациенток с бессимптомной бактериурией. Для успешного лечения беременных с бактериурией на фоне антибактериальной терапии более целесообразно, эффективно, удобно и экономично применять фитокомплекс «НефроБест» по 1 капсуле 2 раза в день с продолжением до 3 мес. Комбинированная терапия с фитокомплексом «НефроБест» характеризовалась более быстрой нормализацией показателей общего анализа мочи и отсутствием роста микрофлоры по результатам бактериологического исследования по сравнению с включением в терапию канефрона Н, что требовало применения более коротких схем.</p>
Without kewood
Interregional Center for Additional Professional Education
Women's consultation MBU "Central City Hospital №7"
Women's consultation MBU "Central City Hospital №2 them. A.A. Mislavsky "
Optimization of therapy of pregnant women with asymptomatic bacteriuria
Journal: Russian Bulletin of the Acoucher-Gynecologist. 2020; 20 (5): 97-102
Kononova I.N., Kuzina T.V., Oparin O.S. Optimization of therapy of pregnant women with asymptomatic bacteriuria. Russian Bulletin of the Acoucher-Gynecologist. 2020;20(5):97‑102.
Kononova in, Kuzina TV, Oparina OS. Optimization of Therapy for Pregnant Women with Asymptomatic Bacteriuria. Russian Bulletin of ObStetrician-Gynecologist. 2020; 20 (5): 97-102. (In russ.).
https://doi.org/10.17116/rosakush20202005197.
Interregional Center for Additional Professional Education
PURPOSE OF THE STUDY
Studying the clinical efficacy of the Nephobest vegetative complex, registered as a biologically active additive, to optimize therapy of pregnant women with asymptomatic bacteriuria (BB).
Material and methods
A survey and treatment of 52 pregnant women with asymptomatic bacteriuria has been carried out. The examination included a bacterioscopic study of the smear on the microflora, a molecular biological study of vaginal content (Test "Femoflorom") and urine (bacteriological research, general analysis of urine), ultrasound of the kidneys. The study of therapy compliance was carried out by the survey of patients. In the 1st group (N.= 32) Along with antibacterial therapy, the drug "Nephobest" was appointed 1 capsule 2 times a day, up to 3 months, in the 2nd group (N.= 20) Along with antibacterial therapy, Kanefron N 2 tablets were prescribed 3 times a day, up to 3 months.
RESULTS
It was revealed that the use of a method of combined treatment of pregnant women with BB using against the background of antibacterial therapy of the plant complex of domestic production "Nephobest" for 3 months led to a resistant and a lack of recurrence.
CONCLUSION
Revealed positive correlation bb bb with bacterial vaginosis (R.= + 0,743 when P.= 0.001) dictate the need to include a survey of the reproductive path and the treatment of patients with asymptomatic bacteriuria. For the successful treatment of pregnant women with bacteriuria against the background of antibacterial therapy, it is more appropriate, effectively, conveniently and economically used by the phytocomplex "Nephobest" 1 capsule 2 times a day with a continuation of up to 3 months. Combined therapy with phytocomplex "Nephobest" was characterized by a more rapid normalization of the indicators of the general analysis of urine and the absence of microflora growth on the results of bacteriological research compared with the inclusion in the therapy of the Canephron N, which required the use of shorter schemes.
Interregional Center for Additional Professional Education
Women's consultation MBU "Central City Hospital №7"
Women's consultation MBU "Central City Hospital №2 them. A.A. Mislavsky "
Pressing dates:
- On approval of the procedure for the provision of medical care for the "Obstetrics and Gynecology" profile (except for the use of auxiliary reproductive technologies) ": Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation of November 1, 2012 No. 572n.
- Bakhareva I.V. Urinary tract infections in pregnant women: prevention and treatment. Obstetrics and gynecology. 2018; 3: 129-137. https://doi.org/10.18565/aig.2018.3.129-137
- Solovyova A.V., Kuznetsova O.A., Ermolenko K.S. Prevention of relapses of infectious diseases of urinary tract and edema in pregnant women by applying cranberry preparations. Obstetrics and gynecology. 2018; 2: 126-130. https://doi.org/10.18565/aig.2012.126-130
- Sangkomkamhang US, Lumbiganon P, Posertcharoensuk W. Antenatal Lower Genital Tract Infection Screening and Treatment Programs for Preventing Preterm Delivery. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015; 2.
- Wing Da, Rumney PJ, Hindra S, Guzman L, Le J, Nageotte M. Pilot Study to Evaluate Compliance and Tolerability of Cranberry Capsules In Pregnancy for the Prevention of Asymptomatic Bacteriuria. J Altern Complegment Med. 2015; 21 (11): 700-706.
- Urinary tract infections in children, adults, pregnant women: cystitis, pyelonephritis, asymptomatic bacteriuria. Clinical recommendations. 2014. https://www.krasotaimedicina.ru/diseases/zabolevanija_gynaecology/asymptomatic-bacteriuria
- Widmer M, Lopez i, Gülmezoglu am, Mignini L, Roganti A. Duration of Treatment for Asymptomatic Bacteriuria During Pregnancy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015; 11: CD000491.
- SMAILL FM, Vasquez JC. Antibiotics for Asymptomatic Bacteriuria in Pregnancy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015; 8: CD000490.
- Szweda H, Jóźwik M. URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS DURING PREGNANCY – AN UPDATED OVERVIEW. Dev Period Med. 2016; 20 (4): 263-272.
- Emptina O.A. Asymptomatic bacteriuria in pregnant women: what evidence-based medicine says. Medical advice. 2016; 4: 123-129. https://doi.org/10.21518/2079-701x-2016-07
- Arkhipov E.V., Sigitova O.N. Urinary tract infections in pregnant women: modern recommendations for diagnosis and treatment. Bulletin of modern clinical medicine. 2016; 9 (6): 109-114. https://doi.org/10.20969/vskm.2016.9(6 ).109-114
- Captile V.A. Urinary tract infection during pregnancy. Archive of obstetrics and gynecology them. V.F. Snegiva. 2015; 2: 4: 10-19.
- Glaser AP, Schaeffer AJ. URINARY TRACT INFECTION AND BACTERIURIA IN PREGNANCY. Urol Clin North Am. 2015; 42 (4): 547-560.
- Souza RB, Trevisol DJ, Schuelter-Trevisol F. Bacterial Sensitivity to Fosfomycin in Pregnant Women with Urinary Infection. Braz J Infect Dis. 2015; 19 (3): 319-323.
- RLS, Nephobist, instruction. https://www.rlsnet.ru/baa_tn_id_99684.htm
- Kravchenko E.N., Gordeeva I.A. Features of the course of gestation and childbirth in asymptomatic bacteriuria in pregnant women: practical experience and therapeutic aspects. Gynecology. 2014; 16: 2: 78-81. https://gynecology.orscience.ru/2079-5831/issue/view/1590.
- Salvatore S, Salvatore S, Cattoni E, Siesto G, Serati M, Sorice P, Torella M. Urinary Tract Infections in Women. EUR J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2011; 156 (2): 131-136.
- Radzinsky V.E., Hapova T.V., Olenev A.S., Soloviev A.V. Cranberry extract in pregnant women with urinary tract infections: efficiency and safety issues. Statuspraenes. 2014; 5: 22-23.
- Naumkina E.V., Abrosimova O.A., Ivanova S.F. Asymptomatic bacteriuria and the condition of the microbiocenosis of sex tract in pregnant women. Infection and immunity. 2016; 6: 3: 77. https://doi.org/10.15789/2220-7619-2016-3.
- SMAILL FM, Vasquez JC. Antibiotics for Asymptomatic Bacteriuria in Pregnancy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015; 8: CD000490.
- Widmer M, Lopez i, Gülmezoglu am, Mignini L, Roganti A. Duration of Treatment for Asymptomatic Bacteriuria During Pregnancy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015; (11): CD000491.
- Wing Da, Rumney PJ, Hindra S, Guzman L, Le J, Nageotte M. Pilot Study to Evaluate Compliance and Tolerability of Cranberry Capsules In Pregnancy for the Prevention of Asymptomatic Bacteriuria. J Altern Complegment Med. 2015; 21 (11): 700-706.
Introduction
Asymptomatic bacteriuria (BB) in pregnant women is a laboratory-determined pathological condition during the gestation period, in which a repeated examination of urine with a break of 24 hours or more reveals in the analyzes the same microorganism in a titer of 100,000 CFU / ml in the absence of clinical symptoms [one]. In 52.3% of pregnant women, asymptomatic bacteriuria is detected in the first trimester, in 35.4% in the second trimester, and in 12.3% in the third trimester [2]. According to WHO recommendations, it is clinically significant to increase the content of bacterial agents to 100,000 or more CFU/ml [3]. According to European researchers, the risk of a complicated course of gestation occurs even with titers from 100 to 10,000 CFU / ml. [4]. Specific factors contributing to the development of latent chronic bacteriuria during gestation are characteristic metabolic, urodynamic changes and mechanical effects: stagnation and reverse reflux of urine due to the reaction of smooth muscle fibers to an increase in the concentration of progesterone and compression of the urinary organs by the pregnant uterus, changes in the chemical composition of urine as a result of physiological insulin resistance, a decrease in immunity leading to the activation of commensals, as well as endothelial dysfunction that occurs against the background of hemostasis disorders in the presence of genetic and epigenetic factors [5]. Due to the presence of adhesins, hemolysin, and other virulence factors, infectious agents colonize the urothelium and lead to the development of various infectious and non-infectious complications [6]. The actualization of the problem is due to the high frequency of asymptomatic bacteriuria in pregnant women, which, according to different authors, is from 25 to 58% [7, 8], its influence on the course of gestation with the occurrence of miscarriage and prematurity, polyhydramnios, edema of pregnant women, infectious diseases of the urinary tract and reproductive tract, intrauterine infection and chronic fetal hypoxia, infectious complications during childbirth and in the postpartum period [9]. Taking into account the risk of complications, microbiological screening is carried out for all pregnant women, and if bacteriuria is detected, antibiotic therapy is prescribed [10]. Semi-synthetic β-lactam penicillins, II-III generation cephalosporins are used as an antibacterial monopreparation. Personification is carried out by identifying pathogens and determining sensitivity to antibiotics [11]. However, after antibiotic therapy in a number of patients, in 45-68% of cases, a recurrence of the process (bacteriological relapse) occurs [12], therefore, the complex of therapeutic and preventive measures includes the use of herbal preparations that have an antiseptic effect on the urinary tract epithelium, as well as diuretic action in dropsy of pregnancy [13].Следует отметить, что растительные уросептики комплексного действия (канефрон Н) имеют длительный положительный опыт применения у беременных для профилактики и лечения бессимптомной бактериурии [14]. Однако высокие дозы (по 2 таблетки 3 раза в день) с отрицательным влиянием на комплаенс * терапии, изготовление препарата на далеких европейских территориях создали предпосылки для разработки оригинального инновационного комплексного отечественного препарата для этиопатогенетического лечения в период гестации, для профилактики рецидивирования инфекционных заболеваний мочевых путей, инфекционных осложнений во время беременности и в послеродовом периоде как со стороны матери, так и со стороны плода. Биологически активная добавка к пище «НефроБест» была создана как улучшенный аналог растительного препарата канефрон Н, она имеет ряд неоспоримых преимуществ. Прежде всего это количественный и качественный состав активных компонентов (табл. 1) [15].
Table 1. Сравнительная характеристика состава фитокомплекса «НефроБест» и канефрона Н
точно дозированный экстракт, мг на 1 капсулу
измельченное растительное сырье, мг на 1 капсулу
Трава розмарин (Rosmarinus)
Трава золототысячник (Centaurium umbellatum)
Корень любистока (Levistici radix)
Листья брусники (Vaccinium vitis-idaea L.)
Следует отметить, что достигнуть точной рецептуры, используя измельченное растительное сырье, невозможно. Поэтому для увеличения биодоступности компоненты растительного комплекса «НефроБест» были выделены отечественными учеными в виде экстрактов, точно дозированы, что позволило достигнуть идентичного состава во всех капсулах.
Как видно из Table. one, количество действующего вещества в продукте «НефроБест» превосходит таковое у препарата канефрон Н ровно в 3 раза. Известно, что лечебный эффект растительных препаратов — дозозависимый и возрастает с увеличением дозировки принимаемого средства. Режим дозирования растительного комплекса «НефроБест» (по инструкции) — 1 капсула 2 раза в день. Для пациентки это гораздо удобнее, чем 2 таблетки 3 раза в день, как у канефрона Н. При необходимости возможно увеличить дозировку для конкретной больной.
Кроме розмарина, золототысячника и любистока исследуемый препарат содержит экстракт листьев брусники. Это в значительной мере усиливает противомикробный, диуретический и противовоспалительный эффект комплекса «НефроБест», предоставляя дополнительные преимущества в сравнении с канефроном Н.
Цель исследования — изучение клинической эффективности растительного комплекса «НефроБест» для оптимизации терапии беременных с бессимптомной бактериурией.
Material and methods
Проведены обследование и лечение 52 беременных (основная группа) с бессимптомной бактериурией. Контрольную группу составили 20 беременных без ББ. Исследование проводилось на базе женской консультации Центральной городской больницы №7 и женской консультации Центральной городской больницы №2 им. A.A. Миславского г. Екатеринбурга.The survey included the collection of anamnesis, generally clinical study, bacterioscopic examination of the smear on the flora, molecular biological study of vaginal content (Test "Femoflor") and urine (bacteriological research, overall analysis, testing of non-County), ultrasound kidneys. All studies were conducted before the appointment of therapy, within 2 weeks after the end of treatment, in a month, after 2 months after the treatment of therapy, after childbirth. The study of therapy compliance was carried out by the survey of patients. Pregnant women were included in the study in accordance with the inclusion and exception criteria. Inclusion criteria: Pregnancy 14-37 weeks; The nosological form of the disease is asymptomatic bacteriuria; Duration of the disease – from one to 15 days; laboratory characteristics – bacteriuria; lack of therapy before the selection into the study; concomitant therapy – personalized antibacterial therapy according to the detected sensitivity to antibiotics; age – 18-45 years; Growth, body weight – without restrictions; Race, nationality, profession, region – without restrictions; The patient's consent to fulfill the requirements of the research protocol. Exception Criteria: Related diseases – decompensated extragenital diseases; Serious violation of the protocol, non-compliance with the patient's requirements of the Protocol and the loss of the subject for observation. In the future, the patient of the main group was divided into 2 subgroups. The distribution of patients in subgroups was randomized – by random sampling. In the 1st subgroup, 32 patients entered, which from the 1st day after establishing the diagnosis "asymptomatic bacteriuria" was appointed the Networkobest vegetation complex for 1 capsule 2 times a day. Initially, this complex was appointed on the basis of antibacterial therapy, then the preparation of another 3 weeks continued. In the 2nd subgroup (group of comparison) included 20 patients, which, from the 1st day after establishing the diagnosis, "asymptomatic bacteriuria" was appointed Kanefron N 2 tablets 3 times a day initially on the basis of antibacterial therapy, then the reception of Kanephron N 3 more weeks. The method of parallel groups was used. The duration of the study was 6 months. Throughout the study, no reception of other phytopreparations was not allowed. The observation of patients was carried out after 14 days, 30, 60 days after the designation of the drug and 1-2 weeks after childbirth for the control of efficiency.
For statistical data processing, standard software packages were used (SPSS 12.0). To indicate quantitative data having a normal distribution, applied: n, m ± m, p ± mP., Ci, δ, where n is the number of observations, M is the average, M is an error of the representativeness of the average, P is the relative indicator (%), MP. – error of the representativeness of the relative indicator, Ci-cumulative intervals, δ – the average quadratic deviation. The accuracy of the differences was checked using the criterion of χ 2 Pearson with the ITSA Amendment. For the critical level of significance when verifying statistical hypotheses in this study, was accepted P.<0.05. To assess the relationship between indicators, the coefficient of rank correlation of the Spirmend was determined. Evaluation of the effectiveness of therapy was carried out with the help of indicators of the relative reducing of risk (OSR) and the absolute reduction in risk (ACR). OSR = (C1-C2) / C1, where C1 is the recurrence rate in the comparison group, and C2 is the frequency of recurrence of the process in the main group; ASR = C1-C2.
Results and discussion
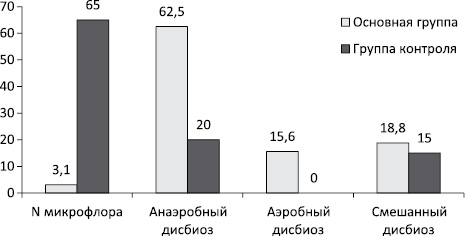
WithThe last age of pregnant women with BB amounted to 27.4 ± 2.2 years. According to the results of a molecular biological study of the vaginal content (the test "Femoflorom") found that in 32 (62.5 ± 5.1%) patients with asymptomatic bacteriuria (95% Ci [54.5 ÷ 76,2]) was identified anaerobic dysbiosis (bacterial vaginosis), which is significantly higher than in the control group (20.0 ± 1.7%, P.= 0.002), and coincides with the data of foreign and domestic researchers [16, 17]. Found high positive correlative connections between BB and bacterial vaginosis (R.= + 0,743 when P.= 0.001) may indicate the predictory role of vaginal anaerobic dysbiosis for asymptomatic bacteriuria during pregnancy (Fig. 1).
Rice. one. The spectrum of vaginal dysbiotic disorders in pregnant women with asymptomatic bacteriuria.
This can be explained by the products of the anaerobes proteases, muds, hemolysin, succinic acid, causing structural and functional damage to leukocytes, violation of their phagocytic ability, a decrease in the catalase and peroxidase activity of vaginal contents [18], which on the background of pregnancy could lead to immunopathological reactions at the local level and Promote the upward infection of urinary tract.
The results of bacteriological (culture) studies of urine in examined pregnant women with the previously identified bacteriuria demonstrated a different species composition of the selected microflora.
Representatives of the family most often saw Enterobacteriaceae. – in 37 patients, which amounted to 71.2 ± 6.5%, 95% CI – [65.3 ÷ 78.9], among the microorganisms of this family, the prevailing species appeared E. coli With 95% Ci – [62.7 ÷ 82,6], which coincides with the results of other researchers [19]. In a minor quantity, gram-negative microorganisms of labor Proteus, Klebsiella and Enterobacter. SPP., Citrobacter. SPP., Pseudomonas Aeruginosa, Acinetobacter and rare types of non-enzyme bacteria (2.5 ± 0.3%). The range of gram-positive microflora was presented Staphylococcus. SPP., Streptococcus SPP., Enterococcus faecalis. Among staphylococci prevalted strains Staph. Epidermidis, Staph. Haemolyticus, Staph. saprophyticus.; Among Streptococci – strains Str. Pyogenes (Fig. 2).
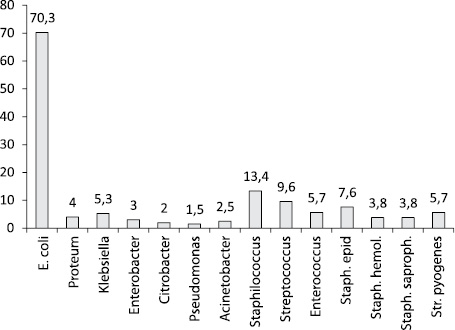
Rice. 2 The range of microorganisms in the urine in pregnant women with bacteriuria according to bacteriological research.
Mixed microflora is isolated in 42.3 ± 3.8%, 95% Ci – [36.9 ÷ 52.1] patients.Among the associations of microorganisms, combinations of intestinal sticks and fecal enterococcus (23.6 ± 1.8%) were predominant; Fecal enterococcus, epidermal and saprophilic staphylococci (33.1 ± 3.2%), less often allocated other mixes, which slightly differed from the results of other studies [20].
According to the ultrasound of the kidneys of changes in the examined patients was not detected.
All patients were assigned antibacterial therapy, according to the results of sensitivity to antibiotics. In the 1st subgroup (N.= 32) Against the background of antibacterial therapy and for 1 month the patient was taken by the complex "Nephobest" 1 capsule 2 times a day. Pregnant 2nd subgroups (N.= 20) Kanefron N 2 tablets were prescribed 3 times a day, the treatment was also 1 month. The subgroups were comparable by age, the number of pregnancies, somatic and obstetric and gynecological history (P.=0,84; P.=0,92; P.= 0.89, respectively).
Analysis of the results of the overall analysis of urine a week after the combined treatment has demonstrated the disappearance of bacteria in the urine in all pregnant women participating in the study. A similar study in a month in the pregnant women 1st subgroup did not reveal changes, 60 days after the appointment of therapy also did not reveal changes in the overall analysis of urine. There was not a single positive result of the culture studies of urine after therapy in this subgroup. According to the results of the study of the overall analysis of urine, the patients of the 2nd subgroup 30 days after the start of the combined treatment in 2 patients (10 ± 0.8%) was retended by bacteriuria, which was significantly different from this indicator in the 1st subgroup (χ 2 = 2,151 at P.= 0.02). Bacteriological examination of urine confirmed in 2 patients of the 2nd subgroup The presence of mixed microflora, which required the continuation of their treatment (χ 2 = 2,150 P.= 0.02). Thus, clinical efficacy in the 1st subgroup was 100%, in the 2nd subgroup – 90.08 ± 8.7% (P.= 0.006), 95% Ci – [81.6 ÷ 97,2].
During the examination in the postpartum period in patients, the 1st subgroup of bacteriuria was not detected, in the 2nd subgroup in one patient preserved bacteriuria (5.0 ± 0.4%), which demanded the conduct of antibiotic therapy and continuing phytotherapy for another 1 month. The recurrence of the BB in the 1st subgroup was not detected, in the 2nd subgroup it was 5.0 ± 0.4%.
An indicator of relative reducing risk (OSR) of recurrence When using the Nephobist plant in combined treatment of BB was 1.0, and the absolute reduction rate of the risk (ACR) recurrence is 10.0 ± 0.7%. The method of combined Treatment of BB using phytocomplex "Nephobest" led to a resistant and lack of recurrence, which turned out to be 5 times more efficient than the use of Kanephron (Table 2).
table 2. Results of the examination of pregnant primary groups after comprehensive treatment