Bubble-ureteral reflux (PMR) is one of the most common diseases of children's age and, at the same time, a clinical term reflecting the pathogenetic mechanism of the disease, based on
Endoscopic correction of bubble-ureteral reflux in children and adults using the drug "Vanatoris"
Bubble-ureteral reflux (PMR) is one of the most common diseases of childhood and, at the same time, a clinical term reflecting the pathogenetic mechanism of the disease, which is based on the unnatural reverse cast of urine from the bladder into the upper urinary tract. PMR is an option for obstructive uralopathy and is accompanied by an affectstructural impact. With a pronounced bilateral PMR, chronic renal failure comes quickly.
Indications for the selection of the method of treatment of this disease remain contradictory. Until the 80s of the last century, all recommendations for the treatment of PMR were reduced to antibacterial prevention or open operations. The emergence of endoscopic Correction of the PMR opened the additional features of the medical strategy.
In modern literature, there are various terms used by the authors to determine endoscopic correction: endoscopic injection, collagenization, endocollagenoplasty, endoimplantation, subureteric Teflon Injection – Sting, Endoscopic subureteral injection, INJECTION OF DIHA, etc.
Endoscopic treatment of bubble-ureteral reflux is a minimally invasive intervention, which consists in transreteral cystoscopic injection of the volume substance in the area of the mouth of the refluxing ureter in order to eliminate urine regurgitation. The mechanism of Correction of the PMR for endoscopic treatment is multicomponent, aimed at eliminating the main causes of the development of an unnatural cast of urine and lies in fixing the mouth of the ureteral in the zone of the urinary triangle, elongation of the short intravenous ureter department and reducing the diameter of the ureter's mouth.
The first medical use of Teflon paste belongs to the Arnold G. otolaryngologist, which used it in order to correct the voice ligament [1,2]. The introduction of Teflon's urological practice occurred in 1974, when Politano VA. Performed the parapereral injection of this drug about the incontinence of urine [3]. For the first time about the positive result of the insufflation of Teflon paste to the area of the refluxing ureter, the child was told Matouschek E. in 1981 [4].
Subsequently, O'Donnell V. in conjunction with Puri P. described the method of endoscopic treatment of PMR [5].
Over the past 30 years, a large number of uruimplants has been tested, starting from Teflon and ending with the cultures of autogenic cells [6-8].The initial experience of using antireflux implants alarmed specialists with cases of side effects: the occurrence of necrosis at the injection site, the risk of malignancy, material migration with the formation of granulomas in regional lymph nodes and (or) parenchymal organs [9,10]. The latest experimental and clinical studies have proven the inertness, hypoallergenicity and safety of modern uroimplants [11-13]. Positive results of endoscopic treatment of VUR, according to foreign studies, reach 70-90% [14-19].
The aim of the study was to evaluate the effectiveness of a modified method of endoscopic correction of VUR using the volume-forming substance "Vantris".
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Our study included 22 children (16 girls and 6 boys) and 7 adult patients (5 women and 2 men) who underwent endoscopic treatment of vesicoureteral reflux with Vantris in the period from January 2010 to June 2012. (Vantris) Promedon. The degree of VUR in these patients ranged from II to IV. In 17 children, VUR was unilateral, in 5 – bilateral. In 5 adult patients, VUR was unilateral, in 2 – bilateral. A total of 36 injections of Vantris were made.
The complex of mandatory preoperative examination included the collection of an anamnesis of the disease, blood and urine tests, urine culture, ultrasound examination of the kidneys and bladder, uroflowmetry, excretory urography, cystography, dynamic nephroscintigraphy. Additional methods included: complex urodynamic study, urethrography (ascending and voiding), gas cystography, preoperative cystoscopy, consultation with a neurologist. Heikkel PE radiographic classification was used to determine the degree of VUR. and Parkkulainen KV. [20]. The cystoscopic picture of the location and shape of the orifices of the ureters used in the work was proposed by Lyon R. [21].
Until 2010, endoscopic correction of VUR was performed according to the standard method. Cystoscopy was performed, during which the clinical and anatomical picture of the bladder was determined: the condition of the bladder triangle, the shape and location of the orifices of the ureter, the presence of paraureteral diverticula and ureterocele, and inflammatory changes. A long injector (diameter 5 Ch) was passed through the working channel of the cystoscope tube, attached to a syringe with Vantris, which is represented by a substance in the form of a hydrogel of a standard volume of 1 ml. The injection needle of the injector (length 6 mm) was carried out under the mouth of the ureter to the full depth. With pressure on the piston of the syringe with the uroimplant, a roller was gradually formed in the area of the needle injection. Depending on the degree of gaping of the mouth and the length of the submucosal part of the ureter, from 1 to 2 ml of the substance was injected. The mouth of the ureter acquired a punctate or slit-like shape, after which the instrument was removed.The bladder was drained by a two-way urethral catheter of Folee 8-14 CH whose cylinder was filled with 5 ml of physiological solution.
The first control examination was carried out 3-4 months after the administration of the drug. In the absence of reflux, the subsequent control examination was carried out in time from 8 to 12 months.
In order to increase the efficiency of the manipulation since 2010, we use the modified technique of injection of the uroimplant, which is as follows: when visualizing the mouth of the refluxing ureter, the string-conductor is installed by 10 cm. The cystoscope is started along the string into the intramural department of the gaping ureter. Against the background of the ongoing irrigation of the fluid, the needle is crushed into the rear wall of the intramural department of the ureter, the cystoscope is given back from the mouth, after which the "Vanteris" gel is insuffling. Visually at this moment there is a lifting of the rear wall of the intramural ureteral department until the mouth is completely wedged. The operation ends with extraction of string-conductor. If there is a patient bilateral PMR, a similar manipulation is performed on the opposite side.
 |
 |
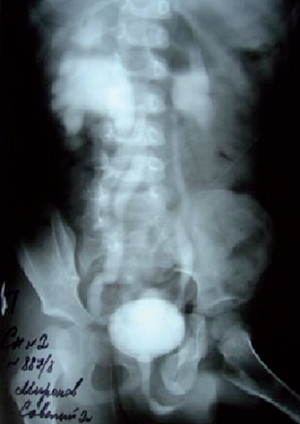
| Rice. 1. Cystogram of the patient M., 2 years 11 months. The active bilateral PMR III degree is determined. On the right clearly visible the Ureter Fissus in the middle third. |
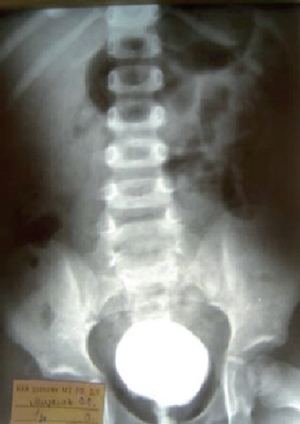
Rice. 2. The mixing cystogram of the same patient 6 months after the operation. PMR is not determined. |
The urinary bubble urban scanning data in the postoperative period demonstrate the elongation of the intramural diver of the ureter on the correction side, while the ureteral emission fraction remains preserved.
RESULTS
In assessing the effectiveness of this technique of endoscopic correction of the PMR, the following results were obtained. According to the control examination (cystography after 3 months), the total liquidation of the PMR after the first injection occurred in 33 observations, which amounted to 92%. In three other observations, a decrease in the degree of PMR (IV ^ II, IV ^ III, IIM) was noted. In the case of detection of PMR I degrees, we continued conservative treatment, and during the control examination after 1 year after the operation of the PMR did not detect. We find explanation for this fact in the theory of "Maturication". In two other observations it was necessary to re-administer "Vanatoris", as a result of which the PMR was eliminated, which was confirmed when performing control cystic cystography.
To illustrate the stated material, we present the next clinical example.
Patient M., 2g.11 months. With a diagnosis: anomaly for the development of the urinary system. Doubling the right kidney (Ureter Fissus in the middle third). Bilatheral PMR III degree. In cystoscopy, two gaping mouths of ureters were revealed. An injection of the Warimplant "Vanatoris" has been performed on both sides of the modified technique. According to the control ultrasonic scanning, the elongation of the intramural department of both ureters, the formation of rollers was revealed. With control examinations after 3, 6 and 12 months, the PMR was not determined.
CONCLUSION
Performing endoscopic correction is an effective way to eliminate VUR. The use of a modified uroimplant injection technique increases the overall efficiency of manipulation up to 92%. The low invasiveness of the method and the absence of complications are the advantages of endoscopic correction. Positive results were obtained both in children and adults, which characterizes the Vantris uroimplant as an effective, safe and reliable volume-forming agent.
KeywordsKey words: children, vesicoureteral reflux, endoscopic correction, volume-forming substances, Vantris.
Keywords: children, vesicoureteral reflux, endoscopic correction, bulking agents, Vantris.
