Detection of heart rate disorders using Holter monitoring ECG: is it always informative? Each practicing cardiologist will agree that the feeling of interruptions in the work
Detection of heart rate disorders using Holter monitoring ECG: is it always informative?
Each practitioner cardiologist will agree that the feeling of interruptions in the work of the heart is one of the most frequent complaints of patients of the cardiac hospital and the cardiac polyclinic department. At the same time, even the most experienced doctor will never be completely sure which heart rate disorders are behind these complaints. That is why today the daily monitoring of the ECG on Holter is still a mandatory study in such patients.
If the rhythm violations are detected, it is worth paying attention to three main questions:
• What is the minimum and maximum ECG monitoring duration for registration of rhythm disorders?
• Two-, three- or twelve-channel recorders (monitors) ECG – what to choose to evaluate ectopic activity?
• What is the minimum and sufficient list of software capabilities?
Duration of ECG monitoring: how long?
This question is asked most often. The most correct is the ECG monitoring of at least 24 and not more than 72 hours. It can be used as
24-hour (more often and preferable) and 72-hour recorder. In the absence of rhythm violations in the first day after a 30-minute vacation, the patient is re-monitored. In the absence of significant rhythm violations for the second day, monitoring continues to 72 hours. In the future, the repeated daily registration of ECG is performed at the discretion of the attending physician.
The question of the need for a 72-hour recorder is also important. Such a registrar can be convenient if the patient describes the relationship of sensations in the work of the heart with concrete stereotypical physical efforts during long-term moves, i.e. In a situation where the patient cannot return to the clinic after 24 hours.
If the patient with complaints about the interruptions in the work of the heart of the rhythm disorder was not detected within 3 days of ECG monitoring, it is worth trying to induce them during the loading ECG test.
Select monitors to analyze rhythm disorders.
At the time of buying Two-channel registrar Additional questions in the analysis of daily ECG, as a rule, does not occur. Some advantage in rare cases have Three-channel recorders: The presence of an additional channel allows you to more clearly differentiate ventricular and sucanementaricular aberrant rhythm disorders.
Usage twelvechnical recorders для выявления нарушений ритма не является целесообразным: исследование становится менее комфортно, но наличие отведений не вносит дополнительной информации о нарушениях сердечного ритма.
Использование двенадцатиканального монитора оправдано лишь в том случае, когда возникает необходимость оценить динамику сегмента ST и связать нарушения сердечного ритма с эпизодами ишемии миокарда.
Необходимые возможности программного обеспечения.
Правильный выбор возможностей программного обеспечения позволяет значительно облегчить и ускорить анализ холтеровской регистрации. Кроме того, врач, имеющий весь необходимый перечень программных возможностей, будет чувствовать себя гораздо увереннее и всегда будет знать, что ничего не пропустил во время анализа регистрации. Именно поэтому к выбору возможностей программного обеспечения необходимо подойти серьезно.
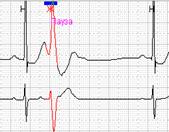
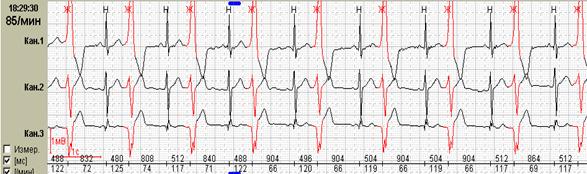
Нередко ощущения перебоев в работе сердца возникают у подростков и лиц молодого возраста с выраженной синусовой аритмией. При этом мы обычно обращаем внимание на ее выраженность и связь с фазами дыхания, которая наиболее отчетливо будет видна при использовании как стандартного выделения фрагмента для печати (рис.1, А), так использования «обзора ЭКГ» (рис. 1, Б).
Fig.1. Пациент К., 17 лет. Дыхательная аритмия в ночное время: стандартное выделение фрагмента для печати (А) и использование «обзора ЭКГ» (Б).
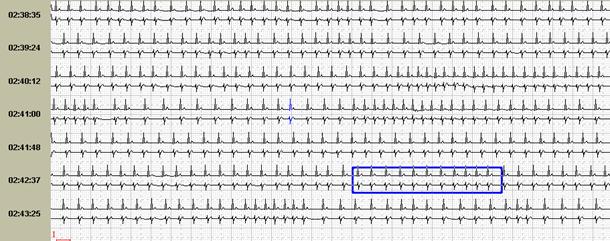
Именно «обзор ЭКГ» позволяет четко дифференцировать дыхательную и недыхательную синусовую аритмию с пароксизмальными суправентрикулярными нарушениями ритма: можно увидеть паузы после пароксизмов ускоренных суправентрикулярных ритмов и стереотипные периоды «гармошкообразного» рисунка с постепенным началом и постепенным окончанием при дыхательной аритмии, как это было представлено на рисунке one.
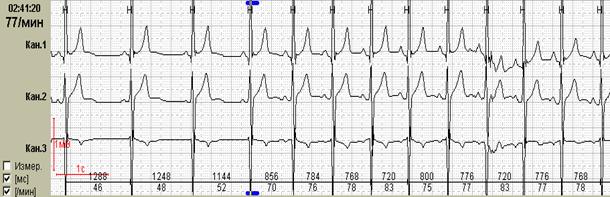
Синусовая брадикардия (правильный синусовый ритм со снижением ЧСС менее 15% от возрастной нормы, что составляет для взрослых менее 60 в минуту) регистрируется во
сне у большинства взрослых здоровых людей, в дневные часы – у профессиональных спортсменов и у лиц с высоким тонусом парасимпатического отдела вегетативной нервной системы. Ее часто приходится дифференцировать с СА блокадой I степени и блокированной предсердной экстрасистолией – нередко дифференциальная диагностика возможна только во время суточного мониторирования ЭКГ. СА блокаду I степени можно заподозрить по внезапному замедлению синусового ритма и такому же внезапному окончанию периода брадикардии, однако достоверно диагностировать это состояние можно лишь при проведении электрофизиологического исследования. Гораздо чаще врач выявляет блокированную предсердную экстрасистолию: регистрируются зубцы Р сразу же после зубцов Т или деформированные двугорбые зубцы Т из-за наложения на них Р зубцов. При этом не наблюдается постоянного интервала РР, как это бывает при АВ блокаде II степени.Эти признаки характеризуют блокированные суправентрикулярные экстрасистолы (рис. 2).
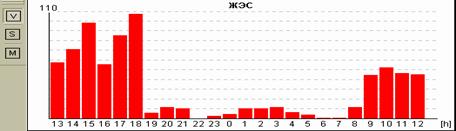
Fig.2. Пациентка Н, 58 лет: А – блокированные предсердные экстрасистолы в ночное время, на их фоне – одиночные интерполированные мономорфные желудочковые экстрасистолы; Б – графики распределения по часам брадикардии и желудочковой экстрасистолии.
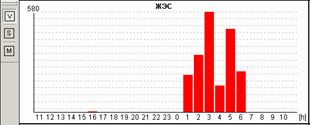
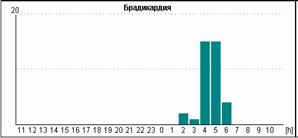
У пациентки Н. на фоне блокированных предсердных экстрасистол выявлена эктопическая желудочковая активность. Особенно важно, что желудочковые экстрасистолы регистрируется именно ночью и только на фоне указанных эпизодов. Взаимосвязь этих событий крайне важна для правильного подбора терапии, поскольку проясняет механизм эктопической желудочковой активности. Именно поэтому предпочтительно, чтобы Ваше программное обеспечение позволяло автоматически построить графики распределения событий по часам.
Некоторые программы вместо графика распределения событий по часам предоставляют пользователям таблицу распределения по часам. На наш взгляд, такая таблица является гораздо менее удобной и наглядной и не позволяет врачу «с первого взгляда» оценить преобладание выявленных нарушений в то или иное время суток.
Важной является также возможность изменения вольтажа полученного ЭКГ-сигнала. Такая возможность особенно необходима, если регистрируется слабо
выраженный, низкоамплитудный зубец Р. Так, например, при смене положения тела в ночное время изменение вольтажа может облегчить диагностику феномена миграции водителя ритма по предсердиям и смены источника автоматизма (рис. 3).
Rice. 3. Пациент А., 77 лет: смена источника автоматизма (короткий эпизод нижнепредсердного ритма из 3 сокращений).
Увеличение общей амплитуды ЭКГ-сигнала приводит к более отчетливой визуализации зубца Р и, следовательно, достоверной диагностике описанных изменений. Кроме того, увеличение вольтажа важно при дифференциальной диагностике пароксизмальных суправентрикулярных нарушений ритма. Так, на рисунке 4, представлена хаотическая предсердная тахикардия с наложившимися на зубцы Т зубцами Р. При отсутствии возможности увеличения вольтажа врачом распечатанные фрагменты тахикардии будут гораздо менее наглядными и вызовут большее количество вопросов у других врачей.
Rice. 4. Больная У., 75 лет: пароксизм хаотической предсердной тахикардии
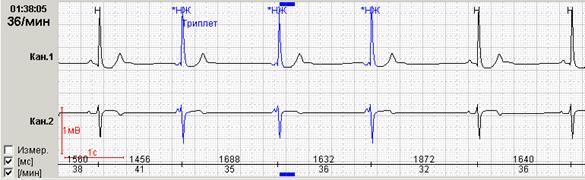
Обязательной является также возможность выделения цветом нарушений ритма различной топографии. На рисунке 5 представлены суправентрикулярные (выделены синим) и желудочковые (выделены красным) групповые экстрасистолы.
Rice. 5. Суправентрикулярные и желудочковые экстрасистолы: А – суправентрикулярный триплет, Б – интерполированные желудочковые экстрасистолы.
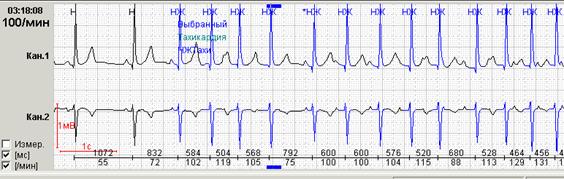
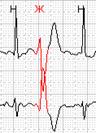
Нередко в холтеровской регистрации встречаются ранние экстрасистолы двух видов: с коротким интервалом сцепления без наслоения на предыдущий зубец Т, а также с коротким интервалом сцепления с наслоением на нисходящее колено зубца Т, т.е. классические экстрасистолы типа R на Т.The ability of programs to allocate Early ventricular extrasystoles (especially with classification In a separate group "R on T") Also greatly facilitate the work of the doctor: using it, you can quickly view the record and calculate the number of such extrasystoles.
Rice. 6. Early ventricular extrasystoles.
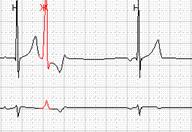
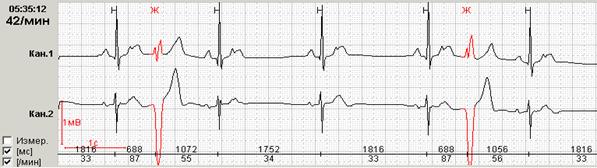
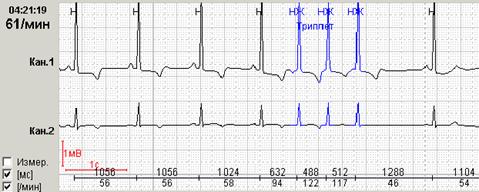
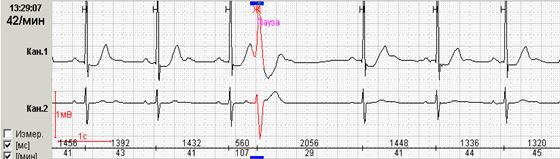
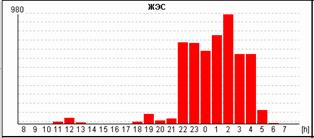
If early ventricular extrasystoles occur against the background of sinus bradycardia, then the subsequent compensatory pause can exceed 2 seconds (Fig. 7a). In this case, counting RR-pauses during the day and the schedule of their distribution by the hour (Fig. 7b) is to reflect in the conclusion and print stereotypical fragments.
Rice. 7. Early ventricular extrasystole "R to T" against the background of sinus bradycardia in a patient with coronary heart disease: a – stereotypical registration fragment; B – the distribution schedule of such fragments during the day with a pronounced predominance at night hours.
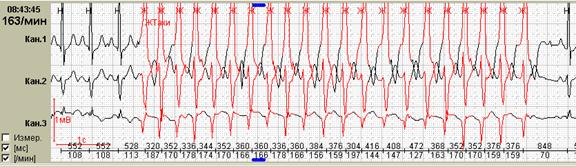
Program's ability With primary automatic analysis to identify ectopic paroxysmal heart rate disorders And their quantitative count is one of the most important possibilities. With their considerable amount during the day, the quantitative counting of paroxysms before and after treatment is important. That is why the acquisition of software without the possibility of identifying and / or quantifying paroxysmal rhythm disorders is extremely undesirable (Fig. 8).
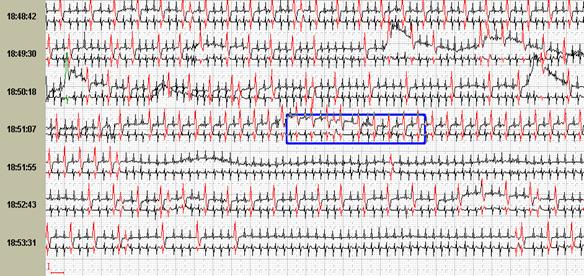
Rice. 8. Patient G., 60 years old, suffers arrhythmogenic dysplasia, B-option "ECG Review" clearly illustrates the frequency of paroxysms.
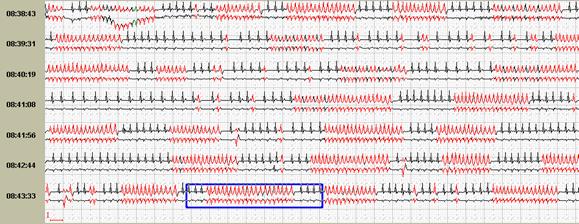
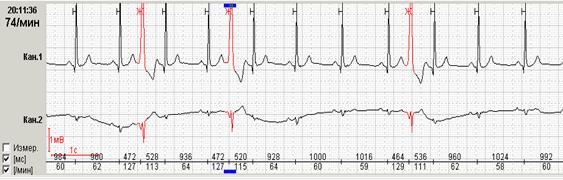
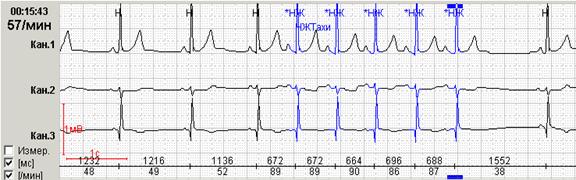
In addition, for patients with paroxysmal ectopical rhythm disorders, the possibility of detecting a pause, excluding them on the screen and markup in the fragment of the absolute value of the pause with their quantitative counting. The features of the "exit" of the next paroxysm – through significant or insignificable pauses – often predetermine the characteristics of the clinical course of the disease with the development of the so-called "arrhythmogenic syncop". Thus, on Figure 9 below, a short paroxysm of the accelerated sunderaricular rhythm ends with a slight lengthening of the RR-interval to 1552 ms, and in a patient with paroxysms of the atrial fibrillation pause exceeds 2 seconds and in the increasing of this value it may cause a syncopal state.
Rice. 9. A short insignificant paroxysm of an accelerated supraventricular rhythm in a patient with a hypertensive disease (a) and a patient with idiopathic paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (b).
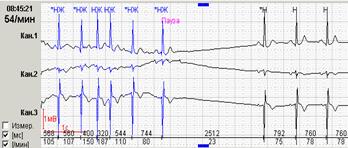
Software features Calculate the number of pauses during the day, build a graph of their distribution and output the absolute value of each pause in the printout fragments, as well as the final consolidated table, are absolutely necessary features in the analysis of daily registration. Often, it is the absolute values of the pauses that show the true cause of the patient's syncope (Fig. 10).
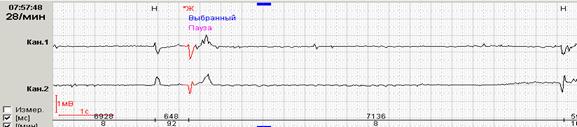
Rice. 10. Hemodynamically significant pauses in a patient with Frederick's syndrome. AF transition to idioventricular rhythm through RR-pause = 7.14 sec (A), then (B) – idioventricular rhythm with pauses up to 5.9 sec.
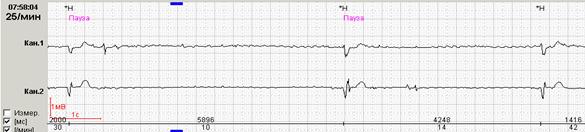
Most of the programs presented by various manufacturers provide the doctor with the opportunity to manually edit the number and duration of both RR pauses and the maximum RR interval. The possibility of such a revision is extremely useful when monitoring the same patient repeatedly (for example, in the dynamic observation of a patient with atrial fibrillation taking a β-blocker).
The software should also allow the clinician to set the absolute value of the RR intervals, which will be referred to as pauses. This is important because the concept of "pause" will differ between adults and children. In adults, both against the background of sinus rhythm and against the background of atrial fibrillation / flutter, pauses are RR intervals of more than 2 seconds. In children, the absolute values of pauses depend on age.
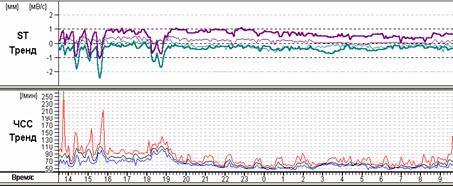
Comparison of various possibilities of a graphic image with each other often significantly changes the view of the attending physician on the tactics of managing a patient. So, for example, Figure 11 shows various screens of the program that expand the understanding of the genesis of existing rhythm disturbances. Stereotypical fragments of allorhythmia (A), clearly visible in the ECG review (B), clearly correspond in time to the periods of walking described in the patient's diary. At the same time, one can see the ischemic dynamics of the ST segment according to trends (C) and the predominance of ventricular extrasystole during periods of wakefulness on the hourly distribution graph (D).
Rice. 11. Patient A., 75 years old. Diagnosis: angina pectoris II functional class. Stereotypical fragments of ventricular bigeminia (A), their large number in the "ECG review" (B), trends in the dynamics of the ST segment, heart rate (C) and a graph of the distribution of ventricular extrasystoles by clock (D) are presented.
The differential diagnosis of ventricular arrhythmias and conduction aberrations according to the His system in atrial fibrillation still causes rather great difficulties during Holter monitoring. So, for example, it is impossible to focus on the presence of pauses due to the irregularity of the background rhythm – atrial fibrillation. Only when compared with other fragments of daily registration, the genesis of which is beyond doubt (in fact, comparison of different fragments “with themselves”), one can draw any conclusion about the genesis of extended abbreviations (Fig. 12).
Rice. 12. Patient N., aged 68: ventricular couplet against the background of atrial fibrillation.
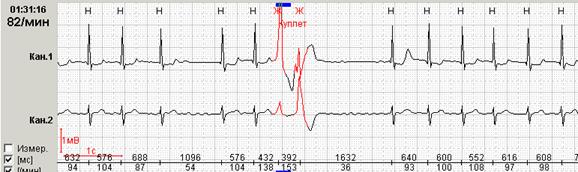
Often, your software automatically detects background fibrillation and/or atrial flutter (as well as paroxysms present in sinus rhythm).Nevertheless, the doctor should necessarily check in the "ECG review", whether all paroxins are revealed with automatic analysis. Currently, almost all existing programs are not capable of full automatic detection of both background flickering arrhythmias and sucanementaricular paroxysms. Unfortunately, the program is not always declared the capabilities of the program correspond to reality in practice.
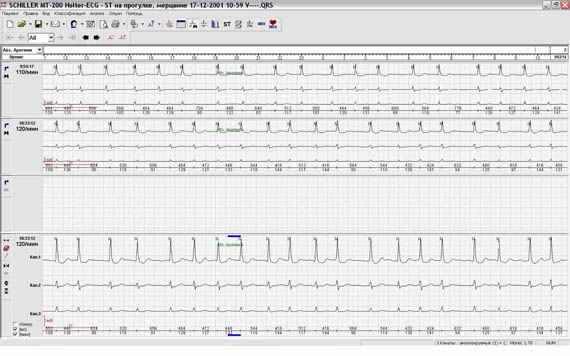
Rice. 13. The program clearly visualizes flickering arrhythmia
In conclusion, I would like to recall that it is the heart rate disorders that are the most frequent indication for holding Holter monitoring ECG. Therefore, when choosing the minimum and optimal software features, you should explore the proposed software especially carefully.
