Complications The development of strictures requires continues to conduct expenses of surgical and endoscopic procedures (bodging, operational treatment, etc.). Each such case follows
Complications
Stricks development requires a continued expensivesoupx surgical and endoscopic procedures (bunning, operational treatment, etc.). Each such case should be considered as a result of inadequate conservative therapy.
Bleeding caused by erosive-ulcerative damage to the esophagus, largely complicates the course of the underlying disease, is found in 2% of cases and directly threatens the life of patients. This complication requires urgent intensive therapy.
One of the unfavorable complications is the formation of Barreta esophagus. In recent years, interest in this problem has increased markedly, which is due to the epidemic distribution of this pathology around the world. This syndrome develops in 10-15% of GERD patients.
Barrette's hypersection of hydrochloric acid, the presence of bile in gastric content, which is an integral part of theLookingEudny reflucktat. Barrett's esophagus is a cylindrical metaplasia of the mucous membrane of the esophagus. Metaplasia can be intestinal and gastric. If the metaplasia is manifested in the form of a cylindrical epithelium of a cardiac or the foundal type of the gastric mucosa, the risk of developing adenocarcinoma is small. An unfavorable prognostic value is the sublictic metaplasia of the mucous membrane of the distal part of the esophagus. The complexity of the diagnosis of Barret's esophagus is the lack of pathognomonic clinical manifestations. The main role in identifying this complication plays an endoscopic study ("flame languages" – the venel-like mucous membrane of the red color). To confirm the diagnosis of Barreta's esophageal, a histological examination of the biopsy of the mucous membrane of the esophagus is produced. This pathology can be argued if at least one of the biopsy is a cylindrical epithelium with the presence of glassoid cells in the metaplazized epithelium. In an immunogistological study, you can identify a specific marker of the epithelium of Barreta – Sukrasisomaltase.
Fast progressive dysphagia and weight loss may indicate the development of the adenocarcinoma of the esophagus. However, these symptoms occur only in late stages of the disease, so the clinical diagnosis of esophageal cancer, as a rule, resets. Consequently, the main way of prevention and early diagnosis of esophageal cancer is the timely diagnosis and treatment of Barreta esophagus.
Diagnostics
The main methods of diagnosis of GERD are esophagel-duodenoscopy (EGDS), carrying out daily monitoring of intra-esophageal pH, radiographic examination, pressure gauge of the lower esophagus sphincter and scintigraphy with radioactive technetium.
Additional research methods: Rabeprazole test, Bernstein test, bilimetry, chromoendoscopy, endoscopic ultrasound examination of the esophagus, etc.
Endoscopic diagnostics is necessary in the initial treatment of the patient and with exacerbation of the disease. However, it does not make it possible to diagnose GERD in the early stages of the disease in an endoscopically negative form, does not allow estimating the frequency and duration of pathological casts of the contents of the stomach in the esophagus. At the same time, the endoscopic method is basic in assessing the state of the mucous membrane of the esophagus (hyperemia, erosion, ulcers, tumor), detecting cardage deficiency, diagnostics of the hernia of the esophageal hole of the diaphragm, the kudardi agenia, anomalies of the esophagus, and the biopsy of the esophagus mucosa with subsequent morphological diagnostics.
Bioptats are taken around the circumference of the esophagus in the region of the gastroesophageal compound. The main morphological criteria of esophagitis are:
– thickening of the basal layer of the epithelium;
– an increase in the number of connective tissue papillas;
– infiltration of epithelium with inflammatory cells;
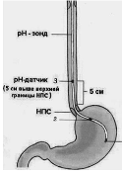
Currently, the most reliable diagnostic method of GERD is the daily monitoring of the Intrapistine PH. This method allows not only to identify and evaluate the nature, duration and frequency of reflux, but also to choose effective therapy. For a reliable diagnosis, the correct internalization of the rh-probe is of fundamental importance. For this purpose, the Ri-Yunda measuring sensor is placed at 5 cm above the lower esophageal sphincter (Fig. 1). Under normal conditions in the lower third of the esophagus pH corresponds to
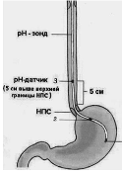
Rice. one. Scheme of the Intrapist Installation of the rh-probation for the diagnosis of GERB: 1 – body of the stomach; 2 – cardiac gastric department; 3 – esophagus
When analyzing the pH gram in the esophagus, it is customary to use the following parameters:
– The total time during which the pH takes values less than 4 units. This indicator is estimated at the vertical and horizontal position of the body;
– The total number of refluxs with pH <4.0 units. per day;
– The number of refluxs with pH <4.0 units. a duration of more than 5 minutes per day;
– the duration of the most prolonged reflux with pH <4.0 units;
– Demeester index is an exposure rate of hydrochloric acid in the esophagus during the entire study time. Normal is considered to be less than 14.72.
Thus, with a pH-metric study, the GER implies episodes in which the pH in the esophagus falls below 4.0 units. Pathological refluxes are considered to be the episodes of "acidification" of the esophagus, which continues for more than 5 minutes and having frequency more than 50 times a day.When conducting an internal pH metry, all indicators are calculated in automatic mode.
We present two clinical observations illustrating the diagnostic efficacy of a long-term intrapure-water pH metry.
The daily intrapure-mode pH gram of the patient K., which suffers from GERD with extensive inflammatory changes in the mucous membrane of the esophagus, propagating more than 75% of the circle, is presented in Fig. 2. When monitoring the Intrapist PH in the patient, 287 GER were recorded, of which more than 5 minutes – 31, the duration of the maximum GER was 32 minutes 10 seconds. Genesed demeester index – 143,41.
In fig. 3 shows the result of a 24-hour pH-metry of the patient S., which suffers GERD with catarrhal esophagitis. During the daily period of the survey, the patient registered 116 GER. GER number for more than 5 minutes
8, and the maximum GER lasted 41 minutes 40 s. The generalized Demeester indicator is 56.15.