Adenoitis in Saratov and Engels treatment at affordable prices! Medical Di Center is modern equipment and high quality services!
Adenoitis
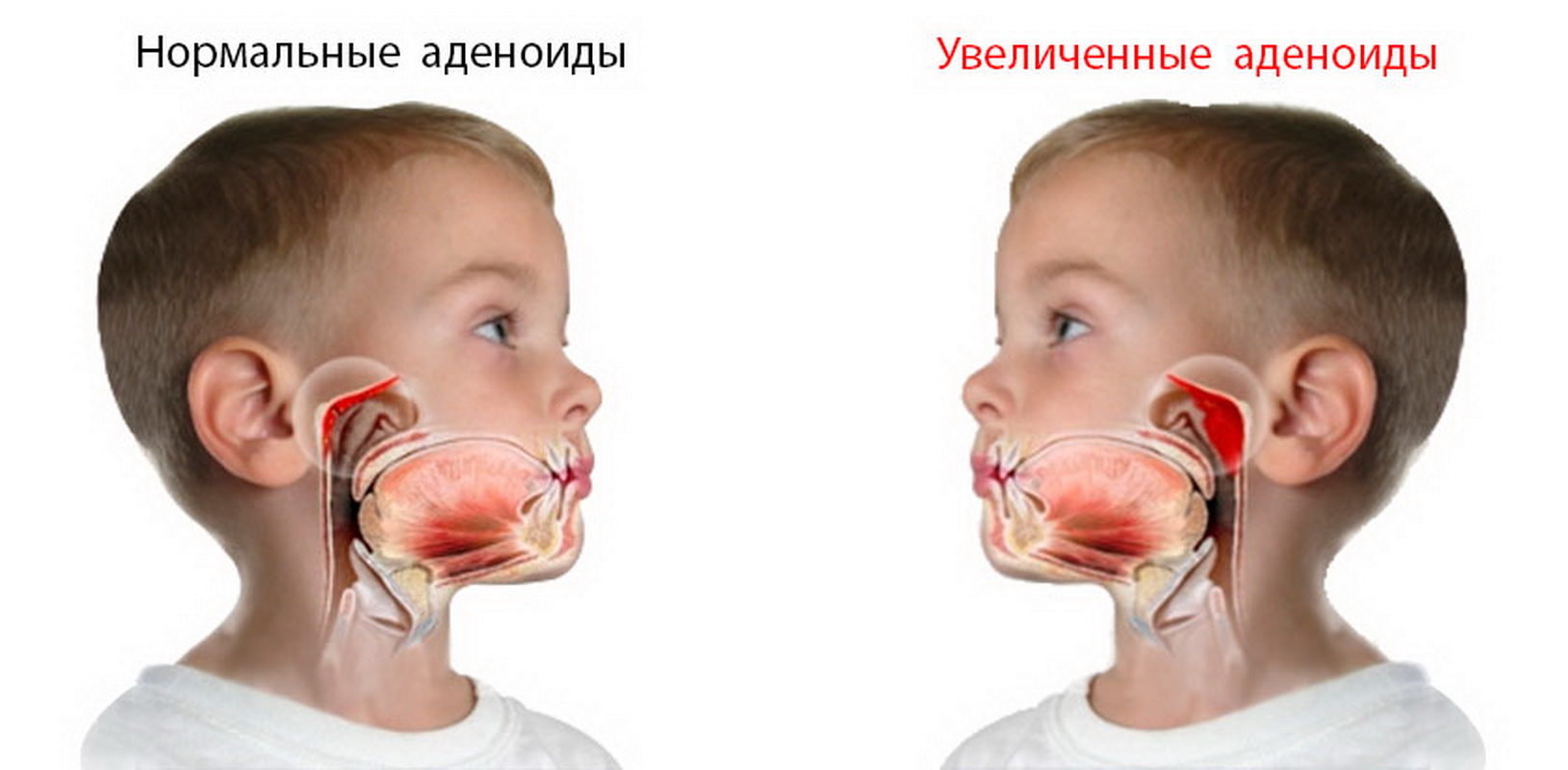
Adenoids are the resulting of lymphoid tissue, which makes up the basis of the nasopharynk almond.
Is your child often and for a long time sick with colds and otitis? It is possible that these are signs of adenoids, where health problems are based on the growth of nasopharynk almond. Adenoids are not visible to the "unarmed" eye – to inspect the nasopharynknyh almond can only LOR doctor with the help of a special mirror.
Adenoids in children, or more correctly – adenoid vegetation (adenoid arrangements) – a widespread disease, manifested from 1 year to 14-15 years. The most often adenoids in the child are manifested between the ages of 3 and 7 years. Currently, there is a tendency to form adenoids in children of earlier age.
Adenoid symptoms in children
The child breathes the mouth, which he is often opened, especially at night.
Nose Noise, and nasal breathing is difficult.
A protracted runny nose that is difficult to treat.
What are adenoids fraught with?
Worsening hearing. Normally, the difference between the outer atmospheric pressure and the internal pressure in the cavity of the middle ear is regulated by the auditory (Eustachiye) pipe. Increased nasopharynk almond overlaps the mouth of the hearing pipe, making it difficult to pass the air in the middle ear. As a result, the drummeal loses its mobility, which is reflected in the auditory sensations.
Frequent colds. Permanent colds are associated with the presence of adenoids in the child, while he cannot breathe a nose freely. In the norm, the mucous membrane of the nose cavity and the apparent sinuses of the nose produces a mucus, which "cleans" the cavity of the nose from bacteria, viruses and other pathogens. If the child has an obstacle to the air current in the form of adenoids, the outflow of mucus is hampered, and favorable conditions are created for the development of infection and the emergence of inflammatory diseases. This is one of the obvious symptoms of adenoids in a child.
Adenoiditis – chronic inflammation of naso-cell almonds. Adenoids, making nasal breathing, not only contribute to the emergence of inflammatory diseases, but they themselves are a good medium for attack bacteria and viruses. Therefore, the tissue of nasopharynk almond, as a rule, is in a state of chronic inflammation. It receives "permanent registration" of microbes and viruses. There is a so-called focus of chronic infection, from which microorganisms can be distributed throughout the body. In case of chronic adenoy, exacerbations are periodically observed with a body temperature lift to 38-39 C.
Reduced academic performance at school. It has been proven that with the difficulty of nasal respiration, the human body is not allowed to 12-18% oxygen.Therefore, in a child suffering from difficulty in nasal breathing due to adenoids, there is a constant lack of oxygen, and, above all, the brain suffers.
Speech disorders. In the presence of adenoids in a child, the growth of the bones of the facial skeleton is disrupted. This, in turn, can adversely affect the formation of speech. The child does not pronounce individual letters, constantly speaks through the nose (nasal). Parents often do not notice these changes, as they "get used" to the pronunciation of the child.
Frequent otitis. Adenoid growths disrupt the normal functioning of the middle ear, as they block the mouth of the auditory tube. This creates favorable conditions for the penetration and development of infection in the middle ear.
Inflammatory diseases of the respiratory tract** — pharyngitis, laryngitis, tracheitis, bronchitis**. With the growth of adenoid tissue, chronic inflammation develops in it. This leads to the constant production of mucus or pus that drains into the underlying parts of the respiratory system. Passing through the mucous membrane, they cause inflammatory processes – pharyngitis (inflammation of the pharynx), laryngitis (inflammation of the larynx), tracheitis (inflammation of the trachea) and bronchitis (inflammation of the bronchi).
Adenoid cough. With adenoids, coughing has no consequences. There are no changes in the bronchi or lungs in patients. Coughing is directly related to irritation of the nerve endings located in the nasopharynx, as well as in the back of the pharynx. Therefore, it is believed that such a cough is caused by reflexes. Cough in this case is a symptom of adenoids in a patient. Very often, doctors do not notice the adenoids and associate the child's cough with a cold or flu. Adenoid cough goes away with the treatment of the adenoids themselves.
These are only the most noticeable and frequent disorders that occur in the body of a child in the presence of adenoid vegetations. In fact, the range of pathological changes that cause adenoids is much wider. These include changes in the composition of the blood, disorders of the development of the nervous system, enuresis, impaired renal function
As a rule, one of these signs of adenoids is enough to establish a diagnosis and carry out adequate therapeutic measures.
Diagnosis and treatment of adenoids
The need for treatment of adenoids is obvious, since prolonged shallow and frequent breathing through the mouth causes abnormal development of the chest and leads to anemia. In addition, due to constant oral breathing in children, the growth of the bones of the face and teeth is disrupted and a special adenoid type of face is formed: the mouth is half open, the lower jaw becomes elongated and sagging, and the upper incisors protrude significantly.
If you find one of the above signs in your child, without delay, contact an ENT doctor who undoubtedly knows how to treat adenoids in a child.In case of detection of grade I adenoids without severe respiratory disorders, conservative treatment of adenoids is performed. The ENT doctor will prescribe how to treat adenoids in a child, for example, instillation of a 2% solution of protargol into the nose, taking vitamins C and D, and calcium preparations.
Treatment of adenoids in children with the help of an operation – adenotomy – is not necessary for everyone. The operation must be carried out according to strict indications. As a rule, surgical intervention is recommended with a significant proliferation of lymphoid tissue (adenoids II-III degree) or in case of serious complications – hearing loss, nasal breathing disorders, speech disorders, frequent colds
If the decision to operate was nevertheless made, new questions arise – is it worth doing the operation under anesthesia or limiting it to local anesthesia, what are the possible complications, how to care for the child in the postoperative period? You can answer them only by weighing all the possible risks and consulting with a competent ENT doctor.
