TREATMENT PATIENTS AT THE OUTPATIENT LEVEL: The following categories are observed at the outpatient level: 1. Asymptomatic patients 2. Mild patients 3. Patients with
TACTICS OF TREATMENT AT OUTPATIENT LEVEL:
At the outpatient level, the following categories are monitored:
1. Asymptomatic individuals
2. Patients with a mild course
3. Patients with moderate course
4. Patients after discharge from the hospital
It is recommended to comply with the anti-epidemic regime in accordance with the SGBP. Patients with mild to moderate illness during home isolation should avoid sedentary behavior, dehydration, and be active (walk) and drink adequate fluids. Relief of fever (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs – paracetamol, ibuprofen, physical methods of cooling) [30, 31].
Patients need to monitor temperature, pulse rate, respiration, blood pressure, saturation (if a pulse oximeter is available). With an increase in clinical symptoms, the assessment of the severity of the condition and further management of patients is determined by the district doctor.
3.1. Management of individuals with asymptomatic COVID-19.
Persons without clinical symptoms at the time of detection of a positive PCR result within 14 days of observation (duration of the incubation period) may develop a disease, therefore they are subject to medical supervision by PHC at home in accordance with the order of the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Kazakhstan (07/09/2020, 10-1- 0/4897-female).
If clinical symptoms appear (fever, cough, shortness of breath, shortness of breath) during the period of medical observation, the district doctor determines the further tactics of managing the patient.
In the absence of manifestation of clinical symptoms within 14 days from the moment of the last contact with a patient with COVID-19, medical observation is removed.
3.2. Management of patients with mild disease hdepends on the presence of risk factors. Persons without concomitant diseases are recommended acetylsalicylic acid at a dose of 75/150 mg per day. If there are contraindications to the appointment of acetylsalicylic acid – clopidogrel 75 mg per day. Individuals with comorbidities should determine the risk of venous thromboembolism using the Padua score or the IMPROVE Risk and Bleeding Model for Therapeutic Patients (Appendix 3). In the presence of risk factors (age over 65 years, obesity, diabetes, hypertension, CHF, etc.), patients require careful monitoring, especially from the second week of the disease.
Patients taking oral anticoagulants for indications (permanent atrial fibrillation, history of deep vein thrombosis, etc.) are advised to continue taking them.
Persons with a mild form of the disease are removed from medical observation in the absence of fever and regression of respiratory symptoms for > 3 days (PCR and CT / X-ray diagnostics are not required).
3.3.Maintaining patients with a medium-imaging form of the disease (before hospitalization in the hospital according to the testimony)
With high risk of VTE (Appendix 3), oral anticoagulants in prophylactic doses are recommended.
The use of anticoagulants on an outpatient level with COVID19.
| № | Average severity in individuals with concomitant (comorbid) diseases | Average severity in individuals without concomitant (comorbid) diseases | Special guidelines for assigning oral anticoagulants |
| 1 | Patients who take oral anticoagulants according to testimony (permanent form of atrial fibrillation, deep vein thrombosis in history and others. Reception of drugs. Continue | Oral anticoagulants (POS): Rivroxaba 10 mg, 1 time per day, for 10 days, or Apiksan 2.5 mg, 2 times in the knocks, within 10 days, or Dabigatran Etexlate 110. mgch 2 times a day – 10 days further conduct control of generally clinical condition, monitoring of many, DDimer, platelets. In the absence of risk of thrombosis based on results (many, DDimer), the transition to Acetylsalicylic acid 75-100 mg (if there are contraindications to the use of 75 mg clopidogrel) under the supervision of the doctor. | – in patients with severe disruption of the kidney function (KK <30 ml / min), the concentration of rivochasaban in plasma can be significantly increased (1.6 times an average), which can lead to increased risk of bleeding; – with caution should be applied to Rivroxaban in patients with a moderate disruption of the kidney function (QC 30-49 ml / min) receiving concomitant preparations that can lead to an increase in the concentration of rivarochasabane in plasma (ketoconazole, ritonavir); – in patients with impaired kidney function light, moderate, or severe with a decrease in QC to 15 ml / min APIKSABAN dose correction is not required; – in patients having KK <15 ml / min, the use of apixabana is not recommended; – with caution to apply Dabigatran Etexlate under states that increase the risk of bleeding: age 75 years and older; a moderate decrease in kidney function (CL creatinine 30-50 ml / min); – with caution to apply with diseases and states associated with increased risk of bleeding, such as: – congenital or acquired chopping disorders; – uncontrolled severe arterial hypertension; – active gastrointestinal pathology with ulcerative formation; – recently transferred acute gastrointestinal ulcer; – vascular retinopathy; – recent intracranial or intracerebral hemorrhage; – intraspinal or intracerebral vascular anomalies; – a newly conducted surgical operation on a head, spinal cord or an ophthalmic surgery; – bronchiectases or episode of pulmonary bleeding in history. – Care should be taken if the patient simultaneously receives drugs affecting hemostasis, such as NSAIDs, platelet aggregation inhibitors or other antithrombotic drugs. |
Persons SO Medical imaging Diseases are removed from medical supervision in the absence of elevated body temperature and regression of respiratory symptoms> 3 days (PCR studies are not required; CT / X-ray diagnostics on shut-offs).
3.4. Maintaining reconvalued COVID-19.
After extracting from the hospital, medical observation of reconvalued secrets undergoing meditative, the serious form of the disease continues at home under the supervision of the doctor of PMS. Terms of observation are determined individually depending on the overall state of the reconstruction. The testimony is carried out psychological and respiratory rehabilitation in outpatient conditions or treatment / rehabilitation in the profile hospital (Appendix 8,9,10).
Indications for planned hospitalization: no.
Indications for emergency hospitalization:
– Fever 38c and higher for 5 days, resistant to antipyretic drugs;
– shortness of breath with ordinary household loads, conversation, increasing nature;
– persons with risk factors (age older than 65 years, SD, AG, etc.) with a moderate severity (ChDD 20-24 in 1 min, SPO2 93-95%, CT1-2 with);
5.1 Non-drug treatment:
Seuming mode (depending on the severity of the flow, the position of the body in bed is desirable, walking on the chamber – under the control of the patient's condition (CH, heart rate, oxygen saturation).
Under the lesion of the lungs, it is recommended that the use of a patient's body position on the abdomen to improve the oxygenation of the lungs with a gradual increase in time (1 hour 4 times a day, to the maximum to 12 hours) – under the control of the patient's condition (CH, heart rate, oxygen saturation), diaphragmal breathing (on well-being), pregnant position on side, knee-elbow position.
The diet is balanced by the content of proteins, fats, carbohydrates, microelements, taking into account the concomitant pathology.
In the initial and in the period of the COVID 19, the methods of physical massage (manual, vibroacoustic, etc.) are not recommended.
Medicia treatment [1,9, 11, 12, 23, 26, 30, 36-40, 41-43, 44-57, 58-65]
Currently, convincing evidence for the effective specific therapy of the disease caused by COVID-19, therefore, the main principle in conducting patients with a confirmed diagnosis of COVID-19 remains optimal pathogenetic treatment, depending on the nature of clinical symptoms, the severity of the disease, the presence / absence of pneumonia ( X-ray and CT / signs), the type and degree of complications associated with diseases, which are carried out in order to facilitate the symptoms and maintaining the functions of organs and systems at a more severe course.
With the light and moderate forms of the disease, abundant drinking in warm form (for the purpose of disinteling, moisturizing mucous membranes is strongly recommended.. At high temperature, a liquid chair is necessary enteral replenishment of the fluid (Appendix 1).
Fever relief (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory preparations – paracetamol, ibuprofen, physical cooling methods).
Intensive care in severe cases (Appendix 1.2). If indicated, infusion therapy is carried out under the control of diuresis (not lower than 0.5 ml / kg / h), saturation, assessment of edema, hematocrit (> 35%). It is necessary to conduct patients in zero or negative fluid balance.
In cases where saturation is less than 93%, it is recommended to start oxygen therapy until SpO2 is reached.2 > 95% with mask or nasal prongs (O flow2 5-10 liters per minute). The combination of oxygen therapy (standard or high-flow) with the patient lying on his stomach in a prone position for at least 12-16 hours a day leads to improved oxygenation.
With a decrease in saturation <90%, oxygenation through a nasal cannula is recommended (FiO2 – 30-40%, ν = 2-4 l / min), prone position;
if after 5-10 minutes the saturation is> 90%, then oxygenation should be continued through the nasal cannula;
if after 5-10 minutes the saturation is <90%, it is necessary to switch to oxygenation through a mask with a reservoir (FiO2 – 50-90%, ν=3-9 l/min), prone position;
if saturation persists <90%, oxygenation through CPAP, high-flow oxygen therapy (including in the prone position) is recommended;
In case of inefficiency (SpO2 <75%), a transfer to protective mechanical ventilation with PEEP is recommended.
Indications for Non-Invasive Ventilation and High Flow Nasal Oxygen (HFNO)
Increasing demand for oxygen
(e.g. O2 flow from 5L/min to 15L/min)
tachypnea (more than 25 movements per minute) –
does not disappear after a decrease in body temperature;
Subjective feeling of shortness of breath
PaO2 < 60 mmHg or PaO2/FiO2 < 300;
PaCO2 > 45 mmHg;
Anticoagulant therapy (ACT)
(prevention and treatment of thromboinflammatory syndrome)
ACTs are recommended for hospitalized In patients with COVID-19, the dose of drugs (prophylactic, intermediate or therapeutic) is selected depending on the risk of thromboembolic complications and the severity of the disease (Appendix 3) [31, 58, 59].
ACT for prophylaxis in severe and critically ill patients
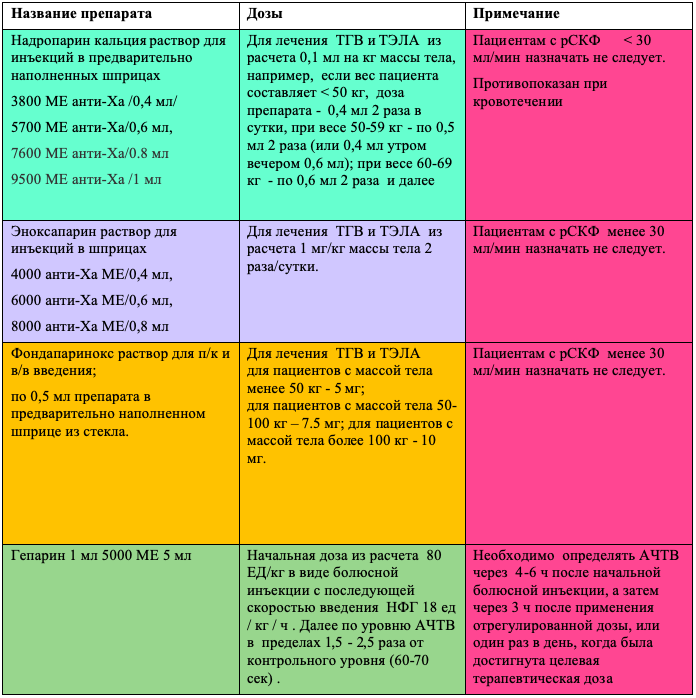
| Name of the drug | Doses | Note |
| Nadroparin calcium solution for injection in syringes – 0.3 ml 2850 IU anti-Xa: 0.4 ml / 3800 IU anti-Xa: 0.6 ml / 5700 IU anti-Xa | Prophylactic dose n / c0.3 -0.4 ml 1 time per day Intermediate dose 0.4 ml 2 times a day s / c, patients with a BMI> 30, a history of VTE, in the presence of active cancer and with an increased level of D-dimer> 4 times | Patients with eGFR < 30 ml/min should not be given. Contraindicated in bleeding |
| Enoxaparin solution for injections in syringes 4000 anti-Xa IU/0.4 ml, 6000 anti-Xa IU/0.6 ml, | Prophylactic dose s / c 0.4 ml 1 time per day Intermediate dose 0.4 ml 2 times a day s / c, in patients with BMI> 30, VTE in history, in the presence of active cancer and with an increased level of D-dimer> 4 times | Patients with eGFR < 30 ml/min should not be given. Contraindicated in bleeding |
| Fondaparinox solution for injection in syringes of 0.25 mg drug of choice for thrombocytopenia | Prophylactic dose s.c. 2.5 mg once a day | Patients with eGFR < 25–30 ml/min should not be given. |
| Heparin 1 ml 5000IU5ml | Subcutaneously 5000 IU 3 times a day | Bioavailability with p / k is up to 30% drug selection with RSKF <30 ml min |
Therapeutic doses of anticoagulantov*
Note: * Appointed only in the case of the confirmed Diagnosis of the TGV and TEL. It is possible that the use of therapeutic doses with special cases of COVID-19 in the absence of a diagnosis of TGV and TELA (for example, during the hard form of the ORDS) after the conservima, but so far evidence is received.
Dosing mode Heparin
| Achtv | Dosing |
| ˂35С (˂1,2 * control) | 80 IU / kg Bolusno, an increase in infusion by 4 me / kg / h |
| 35-45C (1.2-1.5 * control) | 40 me / kg Bolusno, an increase in infusion by 2 me / kg / h |
| 46-70c (1.5-2.3 * control) | Does not change |
| 71-90c (2.3-3.0 * control) | Decrease in infusion by 2 me / kg / h |
| ˃90С (˃3.0 * control) | Stop infusion for 1 hour, then reduce in infusion on 3 IU / kg / h |
Anti-inflammatory therapy (fighting immunophaling syndrome and cytokine storm)
With severe COVID-19, cytokine release syndrome (cytokine storm) is developing, which creates a threat to the occurrence and progression of ORDs, polyorgan deficiency and death. Therefore, it is extremely important to diagnose cytokine storm in the early stages of its development.
– increasing the level of ferritin serum> 600 ng / ml;
– reduction of leukocytes ≤ 3.0×10 9 / l;
– decrease in the absolute number of lymphocytes ≤ 1.0×10 9 / l, the relative content of lymphocytes ≤15%;
– reducing the number of platelets ≤ 180х10 9 / l,
– a rapid decrease in the number of platelets and / or leukocytes (within 24 hours) in more than two times on the background of continuing high inflammatory activity;
– an increase in AST activity;
– reduction of blood fibrinogen ≤ 3.6 mg / l
Clinical signs:
– high fever more than 38C for 5 days, resistant to antipyretic drugs;
– the rapid progression of the process in the lungs with a lesion volume of more than 50%,
Glucocorticosteroids (GKS) [9, 29, 55, 66-68, 79-80]
GKS is not recommended for routine use by patients with a light and medium-quality form of the disease in outpatient conditions (except for applications for other indications), as they suppress adequate immune response and tighten the elimination of the virus and recovery [65].
GCS is recommended in stationary conditions in order to treat severe immunocipal syndrome with severe patients with a threat to the development and manifestation of a cytokine storm for suppressing a hyperimmune response. Dexamethasone can be considered to use in patients with severe COVID-19 in order to reduce mortality [77].
Scheme 1.. Dexametanone At a dose of 6 mg / day for 10 days (B / B, Per OS) is shown for patients at oxygen therapy in high modes, Nivl or IVL [77]. In the absence of dexamethasone, a dose of 6 mg corresponds to 40 mg of prednisolone, 32 mg of methylprednisolone and 160 mg of hydrocortisone (recommended when the adrenal lesions) [78].
Scheme 2. Dexametanone 16 mg w / once a day from 1 to 5 days, 8 mg w / once a day from 6 to 10 day [80].
Scheme 3.. PRednesolon (In the absence of dexamethasone), it is prescribed in a daily dose of 0.5-1.0 mg / kg, parenterally for 3 days with a decrease in dose [78].
Scheme 4.: Mini-pulse therapy with methylprednisolone 250 mg 1 time per day for 3 days. Divide 200.0 ml 0.9% sodium chloride solution.
Scheme 5.. The classic pulse therapy is carried out by methylprednisolone 15-20 mg / kg / day per day for three days [67].
Dissolve at 100-250 ml of 0.9% sodium solution chloride or 5% dextrose solution and introduced for 35-45 minutes. The slower (60-90 minutes) or, on the contrary, fast (10-15 minutes) Introduction is not recommended, since it either significantly reduces the clinical effectiveness of pulse therapy, or can lead to severe complications, up to the development of acute heart failure. [67].
After pulse therapy, the maintenance doses of methylprednisolone are further recommended in a dose of 8-12 mg / day orally, while the duration of therapy depends on the clinical situation [9].
The use of glucocorticoids should be carried out in combination with anticoagulant therapy with low molecular weight heparins. Proton pump inhibitors, antibacterial therapy are recommended according to indications. [nine].
Indications for the purpose of the IL-6 or IL1β receptor inhibitors are a combination of CT OGK data (a significant lesion of pulmonary parenchyma more than 50% (CT3-4) with 2 or more signs):
• CRP> 60 mg / l or growth of the level of SRB 3 times on 8-14 days of the disease;
• Fever> 38 ° C for 5 days;
• The number of leukocytes <3.0×10 9 / l;
• Absolute number of lymphocytes <1.0×10 9 / l
• Blood ferritin level> 500 ng / ml;
• IL-6 level> 40 PC / ml.
Tocilizumab ** (a preparation based on monoclonal antibodies, inhibits IL-6 receptors) is shown for patients with a heavy flow: with acute respiratory distress syndrome, cytokine storm syndrome after determining interleukin-6, ferritin. Concentrate for the preparation of a solution for infusions One-time dose of no more than 400 mg is intravenously drip slowly (for at least 1 hour), with defects, repeat the introduction after 12 hours.
Immune plasma reconvalue chargesPasna Patients COVID-19 in serious condition In the absence of risk of venous thromboembolism (Appendix 3).
The decision to use the immune plasma is made by a medical consultation in the presence of a severe or fast-growing life-threatening current of COVID-19 with one or more features:
– shortened breathing (disposte);
– respiratory frequency ≥30 / min;
– blood oxygen saturation ≤ 90%;
– relations of the partial pressure of oxygen of arterial blood to the fraction of inspiratory oxygen <300;
– development of pulmonary infiltrate> 50% for 24-48 hours;
– need for oxygen therapy;
– Reducing the level of lymphocytes in peripheral blood to 15%.
Consilium reserves the right to use additional criteria for the appointment or abandonment of the use of immune plasma.
The dosage of the immune plasma is established individually taking into account possible complications associated with circulatory overload.The recommended dosage is 1 dose (200 ml) on the first day, 1 dose (200 ml) on the second day of immune plasma therapy (after 24 hours).
It is advisable to start therapy early with the use of immune plasma when transferred to the intensive care unit before the development of decompensation of the functional viability of the main vital organs and systems. The use of convalescent immune plasma should be carried out in combination with LMWH anticoagulant therapy [9].
Intensive care in the development of DN and ARDS (Appendix 1.2).
Currently, numerous clinical trials are being conducted all over the world (such as: RECOVERY, SOLIDARITY, etc.), the final or intermediate results of which allow regular analysis and revision of approaches to the empirical treatment of patients with COVID-19 with experimental drugs with alleged etiotropic efficacy (appointments off-label).
In the current situation, due to the lack of evidence base for the treatment of COVID-19, the use of etiotropic drugs in patients with COVID-19 is acceptable if the potential benefit for him outweighs the risk of their use, and preliminary signing by patients (relatives, guardians, etc.) of informed consent (Annex 7).
Etiotropic drugs are prescribed to suppress viral replication and reduce viral load, and therefore early start of therapy within the therapeutic window (in the first 72 hours from the onset of clinical manifestations to the development of a widespread process in the lungs) is important. With a later admission of patients, the appointment of etiotropic drugs is also recommended, but their effectiveness may be lower.
The use of etiotropic treatment of COVID-19 in comorbid patients requires careful selection of drugs, taking into account drug interactions.
Etiotropic drugs are also prescribed to patients with a probable diagnosis of COVID-19 in provisional hospitals.
Scheme 1
Remdesivir 200 mg IV on day 1, then 100 mg IV daily for 5 days total
Scheme 3
Favipiravir **: 1,600mg x 2p/day on day 1, then 600mg x 2p/day, 7 days
Scheme 1
Remdesivir 200 mg IV on day 1, then 100 mg IV daily for a total of 10 days for ventilated and ECM patients
Notes:
* treatment regimens that include experimental etiotropic drugs are prescribed to the patient only upon signing the informed consent (Appendix 4) personally or by his legal representative as part of participation in a clinical trial. If it is impossible for a patient to conduct or participate in a controlled clinical trial, the use of experimental drugs is possible on the basis of the principles of humanism, when the benefits of the use exceed the risk of consequences and only if the patient or his legal representative signs an informed consent to the use of experimental treatment, taking into account possible side effects.The use of an experimental drug or intervention is carried out in exceptional procedure under observation, and the results, including side effects, are recorded and are published in a timely manner and communicated to inform the broad medical and scientific community (https://www.who.int/ru/news-room/ COMMENTARIES / DETAIL / OFF-LABEL-USE-OF-MEDICINES-FOR-COVID-19).
** Faviupampi security (FP) has not yet been properly studied. FP is contraindicated to women with a well-known or alleged pregnancy due to teratogenicity. Women of childbearing age should conduct a pregnancy test. FP has cardiotoxicity (the risk of the development of the elongated Qt syndrome). Dyspeptic phenomena, increased hepatic transaminases, reduction of blood neutrophils,
Antibacterial therapy at COVID-19: The viral lung damage at COVID-19 is not an indication for starting empirical antibacterial therapy. The assignment of the ABT is shown when the secondary bacterial pneumonium is connected (the appearance of purulent sputum, the increase in prothcitonin, CRH), with exacerbation of chronic foci of infection, against the background of GKS, Tocilizumab, the attachment of bacterial complications of any localization, when conducting invasive events, veins, IVL, ECMO, etc. . (Empirically / and / or taking into account the sensitivity of the allocated strain) (Appendix 8).
Treatment of comorbide diseases, states and complications is carried out in accordance with the clinical protocols of diagnosis and treatment according to these diseases, states and complications (Appendix 7). Algorithm for dynamic observation of patients with chronic diseases, including persons 60 years and older during a period of disadvantaged epidemiological situation on COVID – 19 (Appendix 12).
ACE inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers: Patients having a concomitant pathology of the cardiovascular system (or other indications) against the background of COVID-19, which the EAPP and WHOPs were prescribed, should continue to receive these drugs [56] (Appendix 8).
Statins: Patients with COVID-19, which are prescribed by the statin therapy for the treatment or prevention of cardiovascular diseases, must continue to receive these drugs [64] (Appendix 7).
NPBS: Patients with COVID-19, which take the NSAID to treat the concomitant disease, must continue previously assigned therapy [64] (Appendix 7).
Operal Vitamin-K independent anticoagulants (PC) Patients originally obtained, replace the introduction of therapeutic doses of NMG due to significant drug interaction with etiotropic drugs.
Inhalation corticosteroids: Patients with COPD, asthma, allergic rhinitis is recommended to continue the prescribed inhalation corticosteroids. The use of nebulizer therapy, if necessary, should be carried out in a separate room with negative pressure [64] (Appendix 7).
