Eosinophilic cationic protein (ECP) is a positively charged protein that has basic properties and is part of the cytoplasmic granules of eosinophils.
Eosinophilic cationic protein
Eosinophil cationic protein or eosinophilic cationic protein
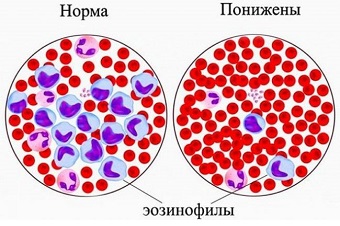
Eosinophil or eosinophilic granulocyte called one of the types of leukocytes (immune blood cells), which protects the body from parasitic infections and prolonged exposure to biologically active components that cause allergic reactions.
They got their name because when staining cells in a blood smear according to the Romanovsky method, eosinophils are not sensitive to the main dye, but they get intense staining with acidic eosin.
- preventing the processes of degranulation into the surrounding tissues of cells involved in hypersensitive reactions (basophils and mast cells), and associated pathologies – bronchial asthma, allergic conjunctivitis, rhinitis and dermatitis;
- counteracting the toxic effects on the nervous system of parasitic organisms (for example, helminths);
- inhibition of the growth of tumor cells;
- bactericidal and antiviral activity.
The concept of eosinophilic cationic protein (ECP)
EKP is a protein that is secreted by eosinophilic granulocytes into the surrounding tissues during inflammation and has a local cytotoxic effect, including on various bacteria and parasites, on endogenous cells, incl. on the epithelium of the respiratory tract.
At the moment of activation of eosinophils by immunoglobulins and cytokines, they are degranulated (the internal content of granules enters the bloodstream system). The presence of CPE in the blood is directly proportional to the volume of eosinophils.
The most common pathologies associated with the activation of eosinophilic granulocytes are immediate allergic reactions. They are also known as type 1 allergies and include conditions such as hay fever, asthma, neurodermatitis, which can occur with certain allergic reactions to bee pollen, dust mite allergens, insecticides, animal dander, and more.
In addition, an allergic shock reaction (called anaphylaxis) can contribute to the development of acute and life-threatening asthmatic attacks. Such a severe course can occur in connection with a food allergy or an allergy to insect venom.
Medical significance of screening
Eosinophilic granulocytes play an important role in the pathogenesis of bronchial asthma. There is a close relationship between the number of eosinophils and the concentration of ECP.
Determination of ECP in the blood may also be useful in assessing the health status of patients with severe forms of type 1 allergy in order to analyze therapy or response to specific treatment.
The diagnostic significance of calculating the amount of ECP in the blood lies in assessing the level of manifestation of eosinophilic inflammation. The KPI indicator depends on the severity of the allergic manifestation. Dynamic control over the concentration of ECP in the body in patients with bronchial asthma makes it possible to predict spontaneous attacks, determine the aggravation of the patient's condition, and monitor the effectiveness of treatment.
Another area of ECP use is the detection of DRESS syndrome, which occurs due to drug resistance. This pathology is manifested by rashes on the skin, damage to internal organs, an increase in eosinophils in the blood. Very often, this syndrome is diagnosed during NSAID therapy, in particular co-trimoxazole, phenobarbital, penicillin and sulfonylurea drugs, and phenytoin.
Indications for the test

In severe allergic manifestations, the measurement of CPE in the blood can be prescribed for the purpose of:
- monitoring of the inflammatory process;
- the effectiveness of therapeutic measures (for example, cortisone therapy);
- confirmation of compliance by the patient with the prescriptions for the dosage of drugs prescribed by the doctor.
The test makes it possible to analyze eosinophilic inflammation in the case of dermatitis, bronchial asthma, allergic rhinitis, autoimmune diseases. In the case of an allergy, the concentration of ECP is considered a more sensitive criterion than the number of eosinophils in the blood, the titer of which can increase at normal values of the number of eosinophils.
General information about the study
- skin itching;
- necrosis of the bronchial epithelium;
- increased secretion of mucus by the bronchi;
- toxic effect on the heart muscle.
In modern medicine, much attention is paid to the DRESS-syndrome (drug intolerance), which is characterized by rashes on the skin, damage to internal organs and deviations of the leukocyte formula (the presence of a large number of eosinophils). Eosinophil cationic protein levels are elevated in patients with this syndrome.
To whom and when can a specialist prescribe a study?
- allergic dermatitis – dry itchy rashes on the skin;
- atopic rhinitis – sneezing, swelling and itching of the nasal passages, runny nose;
- food hypersensitivity reaction (with the use of milk, nuts, cereals, eggs, seafood, citrus fruits) – swelling and itching of the oral and pharyngeal mucosa, urticaria, coughing, sneezing, nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, abdominal pain, lowering blood pressure;
- bronchial asthma – cough and asthma attacks.
Analysis methodology
Biomaterial for research – blood plasma without fibrinogen, selection is made from a vein in a medical institution.
- The day before the test, exclude physical and moral stress.
- Dinner until 21:00, alcohol is prohibited.
- In the morning, do not breakfast, do not smoke, you can drink water.
- On the eve of the test, the test should be coordinated with the physician therapy (if the reception of drugs was prescribed on an ongoing basis). Since some drugs can distort the results of diagnosis, the reception of such drugs should be discontinued a few days before the study.
In accordance with the methodology developed and approved by the laboratory center, the method of sample of solid blood to determine the ESR is subject to centrifugation and decanting after 60-120 minutes from the date of the sample on the analysis. The definition of the CPE concentration is not suitable for separate self-screening of diseases, mainly this study is used as a marker of control therapy.
Deciphering data analysis

The normal concentration of the ESR in the blood: from 0 to 23 ng (nanograms) / ml.
- allergic dermatitis, otitis, ritin, conjunctivitis;
- bronchial asthma; ; ; ;
- severe bacterial infection;
- Dress syndrome;
- autoimmune pathology with the presence of eosinophilic inflammation.
Factors that affect the results of diagnostics
Monitoring the amount of KPE allows you to control the mechanism of the course of the disease and predict the progression of asthma attacks, evaluate the effectiveness of therapy, and regulate the acceptable dose of medicines.
Under the influence of certain criteria, the parameters of the KPE can be unreliable. As a rule, this happens when using some drugs, including NSAIDs.
At the same time, the high amount of ECP is often observed with malignant, benign formations in the kidneys, acute form of bacterial sinusitis, with helminths, etc. The test results must be evaluated in conjunction with the indicators of additional studies of differential diagnosis.
An allergic process does not always affect the increase in ECP titers. To establish the cause, calculate the level of exposure to the stimulus, you can only by dynamic control over protein proteins of eosinophils in patients. In order to competent interpretation of the laboratory conclusion and adjustment of the treatment regimen (if necessary), contact a specialist.
How to properly interpret the values of the ESR in the blood?
The ESR values above 15 μg / l are considered elevated and are an indicator of strengthened activation of eosinophilic granulocytes in the composition of the allergic inflammatory process of the 1st type.
Often, patients have significant oscillations of the KPE values in the blood, which depend on the set of different factors. It is this reason that is a good reason in order to consider the analysis on ECP is not quite informative. Therefore, in order to observe the inflammatory process or for the effectiveness of treatment, this test should be carried out either for a long time or in a complex with other studies.