The features of medicine of ancient India in the Vedic era are little known. There are scarce data in the "Rigveda" about three diseases: consumers, pumping and bleeding. In some sections, "Rigveda" describe the magical rites of healing. For the Vedic period, the intertwining of therapeutic knowledge with magical rites and religious beliefs.
Medicine Ancient India: historical facts, features
The first memories of the state, located in the valley of the fertile River ind, belong to the 3 millennium BC. e. The sacred river gave the name of the vast country of India, which is not inferior in the magnitude of its cultural heritage such foci of civilization as an ancient Egypt and the state of Mesopotamia.
In the Indus Valley, houses were built clearly on the plan. The wellms were cut in the most right places, which were laid by burnt bricks. Brick were used in the construction of walls of houses. The city's wastewater system went out drainage pipes. Nowhere is no longer known such an ancient civilization, equipped with such a functional drainage system.
But such highly developed sanitary facilities are uncharacteristic for subsequent periods of development of ancient India, then there is only a decrease in architectural developments. The doctrine believes that this is due to cataclysms: droughts and floods, as well as in the exhaustion of internal resources.
But today is not about the formation of India as a state, but on the development of medicine of this country. Where was the best pharmacy and medicine of the ancient world developed? India, China – It is here that the first medical knowledge is taken here. Some of them cause admiration and in the modern world. Many are relevant today.
Next, we describe what medicine was in ancient India, briefly. The most important thing is to read about it in our review.

Formation of ancient Indian philosophical knowledge
2 thousand BC e. The first ancient Indian philosophical ideas are formed. They reached our days in the form of literary monuments, which received the common name "Vedas". Here are collected ancient hymns, chants, spells, and so on. Vedas – the first attempt of a person in philosophically to interpret the environment. Although here you can find half mythical and superstitious interpretation of the environment of a person, but this work is the first prefilosophically source.
In Ancient Indian philosophy, a variety of views were mixed, where idealistic and materialistic trends are visible. Basically, it contains the basic idea of the world soul, which is in the process of self-development. It is the global soul that encourages the primatory to create a material world, including a person. Philosophy and medicine of ancient India were inseparable. It was believed that the human body is an external shell of the immortal soul, which is part of the global spirit.The disadvantage of the spiritual essence is the extreme attachment to the world of materialism, therefore, by nature, a person is imperfect. This is the reason for his bodily problems.
Chinese medicine regarding philosophical teachings
Advances in Indian medicine have had an impact on Chinese medicine. Ancient Chinese philosophy is characterized by a development path from the worship of natural elements to constructive religious and philosophical structures – Confucianism and Taoism, as well as to natural philosophy. The concept of the development of the world by Chinese philosophers laid the foundations of medicine and the concept of the causes of disease. From very ancient times, ideas about anatomy began to form. But in the 2nd century BC. e. Confucianism was approved, so the dissection of corpses fell under the ban. According to Confucius, the human body should remain intact and be returned to the parents intact. Therefore, the knowledge of the anatomical features of the body among the ancient Chinese lagged behind the ideas of the ancient Indians.
Ideas about diseases and health in ancient China were based on traditional concepts of philosophy. Traditional Chinese medicine associated human organs with the fundamental principles of yin or yang. Yin was responsible for the health of the Zang organs – the heart, liver, lungs, spleen and kidneys. Yang was given six fu organs: the stomach, gallbladder, bladder, large intestine, small intestine, and three heaters. Heaters were called a system for maintaining internal heat, depending on digestion, respiration and urination. In the human body, yin and yang should be in harmony, and with illness, the balance was disturbed.

The origin of medicine in the Vedic era
Features of medicine of Ancient India in the Vedic era are little known. There is meager information in the Rig Veda about three diseases: consumption, leprosy and bleeding. In separate sections of the Rig Veda, magical rites of healing are described. The Vedic period is characterized by the interweaving of healing knowledge with magical rites and religious beliefs.
Mythological characters in the Vedic religion are associated with the concepts of health, disease and healing. All representations of the ancient Hindus are described in the Atharva Veda. Here is collected all the folk experience in healing with herbs, but to cure the disease, you need to pray, cast spells and make sacrifices. Bhishadsh, or "exorcist", is the very first designation of an Indian healer. Gradually, the caster turned into a healer, but the name remained the same. Also, the concepts of the causes of diseases have changed dramatically.
Ayurvedic knowledge
The development of medicine in ancient India began at the beginning of our era. Then came the system of healing Ayurveda, or "the doctrine of long life." A small group of people – vaidyas – outlined the first experiments in healing and healing. They were children of nature, lived among mountains and forests.The Vaidyas closely connected man with the Universe, considered him a particle of cosmic energy, in their opinion, man embodies the five primary elements, as well as higher powers and elements. They noticed the dependence of people on the lunar cycles, and also believed that every organ in the human body has an analogue among animals or plants.
Ayurveda received a very wide recognition and gradually spread to the territory of the East. Ayurvedic knowledge gradually changed, but existed everywhere. Sometimes it is referred to as Chinese medicine, but this is not true. The Indian philosopher in his work gives practical advice and describes acupuncture, or acupuncture. A long time ago, even during Dhanvantari, in the treatment of diseases, they used acupuncture and hirudotherapy, that is, the use of leeches, they also did plastic surgery and performed organ transplants. For Ayurvedic methods in the treatment, multicomponent herbal preparations were widely used. Each plant occupies a specific niche and is used to achieve the desired result.

The first concepts of the life of the organism
The medicine of ancient India in the classical period of the country's history changes ideas about the origin of diseases. There is a new round in the development of medicine – the supernatural causes of diseases that dominated the Vedic period are thrown into the past. From now on, man was considered as a particle of the environment. Now, according to the ideas of the ancient Hindus, it consisted of the elements of fire, earth, water, ether and air. The functioning of the body was associated with the connection between fire, air and water, which carried three fluids: bile, wind and mucus (bile – between the navel and heart, wind – below the navel, mucus – above the heart). Three fluids and five elements together formed 6 organic products of the human body: muscles, blood, bones, brain, fat and male seed.
The wind carries coolness and freshness, sound and air currents. It is responsible for excretion, digestion, circulation and metabolism in the body. If the wind slows down, then the circulation of juices and substances stops and the normal vital activity of the body is disturbed.
Medicine of Ancient India is based on the following knowledge:
- Phlegm in man and space was a soft substance, it acted like a lubricant, covered all uneven and rough surfaces, was responsible for movement and interaction.
- Bile is a fiery element responsible for the temperature regime in the body, for the activity of the heart muscle and for the normal activity of the digestive tract.
- In violation of the interaction and the normal flow of mucus, wind and bile, the disease began. Its heaviness and seriousness was determined by the degree of imbalance between the three most important primary elements.

Reasons for the rapid development of medicine in ancient India
What are the features of the development of medicine in ancient India? No wonder it got its second name – the country of sages, because it has always been famous for its healers, who became known far beyond the borders of their native land. From Buddhist legends, through the prism of centuries, information came about the ancient healers: Charak, Jivak and Sushruta.
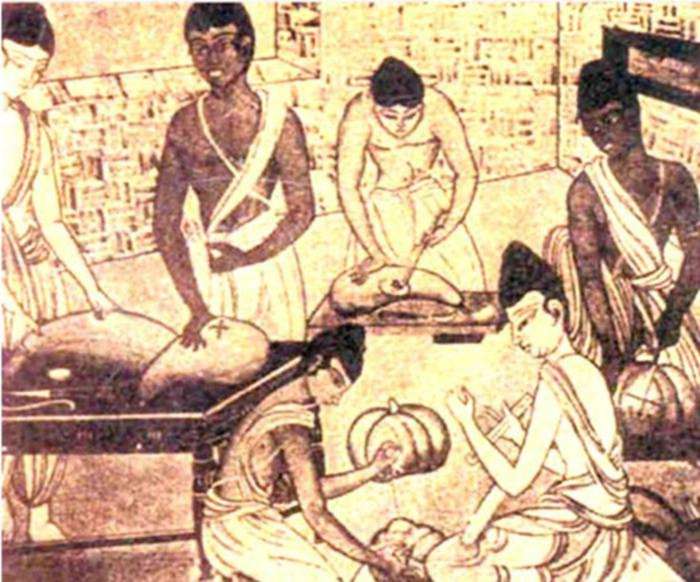
The monuments of Ayurvedic literature of that time include "Sushruta Samhita" and "Charvaka Samhita". The first of them is the oldest treatise on surgery, which describes more than 300 operations, 120 medical instruments and 650 medicines.
Ancient Indian healers had the most extensive knowledge about the structure of the human body. Religious canons did not prohibit the study of corpses, it was enough to atone for their actions by looking at the sun, touching a sacred cow, or using a bath for cleansing.

A huge contribution to the development of medicine of the healer Sashutra
Confucianism and medicine of Ancient India at the time of the healer Sashutra no longer had anything in common, since surgery began to develop. And Confucius, as we remember, was against the violation of the integrity of the human body. For Sashruta, surgery became the first and most prominent medical science. Under him, the Indians mastered the manufacture of surgical instruments from steel, unlike other peoples who use bronze and copper for the manufacture of instruments. Ancient blacksmiths knew how to make them sharp, comfortable in the hand and capable of splitting hair. The names of the instruments mentioned tigers, bears, lions, deer, wolves and many types of insects. Their teeth, trunks and claws became the model for scalpels, needles and forceps. And before the operation, the surgeon asked for strength from these animals, but did not forget to disinfect the instruments by calcining on fire, washing with hot water and juices of special plants.
Ancient Indian surgeons used fixed bandages, tractions, and bamboo splints for fractures; stitched the edges of the wounds with hemp and linen threads; bleeding was stopped by cold and ashes; ulcers, tumors and burns were treated according to a special technique. Even then, they began to use henbane, wine, hashish, opium and Indian hemp for pain relief.
Indian surgeons have successfully performed plastic surgery on the face. They were engaged in the restoration of lips, nose and ears (they were lost by court order or in a fight).
Sushruta's treatise describes in detail the method of rhinoplasty, which was called the "Indian method" and, with some changes, has been successfully used to this day. In ancient Indian texts, you can get acquainted with the methodology for performing cataract surgery.
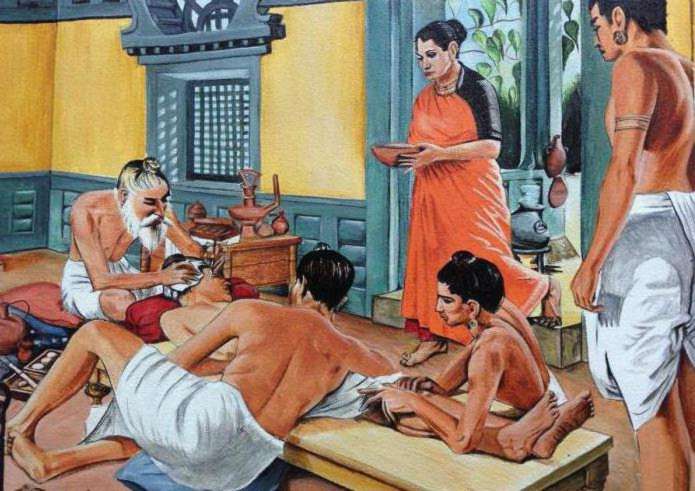

Medicine of Ancient India: Schools of Medicine
It is surprising to learn about the advanced Sushruta school at that time, which had special laboratories where medicines were made, operating rooms, as well as separate rooms for theoretical and practical classes.When studying with Sushruta, the followers were supposed to use devices resembling diseased organs. To get acquainted with the bleeding, the shoots of water lilies were used, the extraction of solid bodies was learned on the fruits of panas, the art of dressings was trained on mock-ups. When teaching medicine, the student had to study philosophy, pharmacology, botany, chemistry, biology, and also master medical skills.
The formation of the medical profession in ancient India
The attitude towards the doctor in ancient India was ambiguous throughout history. In the Vedic period, the profession of a healer enjoyed respect and reverence. But with the development of the caste system, the situation changed dramatically, with the appearance of inequality, some occupations were brought into the category of unclean, and those who practiced them were declared untouchable. Healers fell into this category, next to them were acrobats, carpenters and those who care for horses. But still, from the ancient texts you can find out that the practice of healing was held in high esteem.
Among the leading healers of Ancient India were monks, and the monasteries themselves became centers of healing. It was permissible for the monks to provide medical assistance to those in need, this was their destiny and grace.
Yoga is a way to look into yourself
The medicine of ancient India was intertwined with religious and philosophical teachings, especially with yoga. It combines moral and ethical teachings, religious philosophy and a set of trainings (asanas). To comprehend the teachings, it is necessary to undergo a two-level training: comprehension of the spirit and physical yoga. For mental and physical health, it is necessary to keep the body and thoughts clean, and also be able to relax completely. Yoga still enjoys unprecedented popularity and has many followers.
Ancient Indian healing centers
The medicine of Ancient India (a brief history of formation is presented to your attention in the article) at that time provided for original centers of healing. The city of Taxila was one of the centers of medical education in ancient India. The student had to thoroughly possess not only theoretical knowledge, but also boldly use it in practice. After the teaching, the teacher gathered his students together to give a special instruction.
Directly the right to heal should be issued by the rajah. He was engaged in monitoring the work of doctors, and monitored the observance of medical ethics. The doctor was supposed to always be neat and clean, wear perfumed clothes, cut his beard short, always keep his nails in order, leave the house with an umbrella and a stick, and most importantly, not tell anyone about the condition of his patients. There were rules according to which the doctor did not take payment from the poor, brahmins and friends. And if a wealthy person refused to pay, he was charged part of the property.For incorrectly prescribed treatment, a fine had to be paid.
The history of medicine in Ancient India tells that for the ancient Indian culture, the main distinguishing feature was the veneration of knowledge. From many countries, young healers came to India to gain experience. Universities were opened in the cities, where they paid attention to the study of astronomy, mathematics, astrology, religious and philosophical texts, Sanskrit and medicine.
The history of medicine in ancient India is summarized in this material. We hope that the information was interesting and useful for you.
