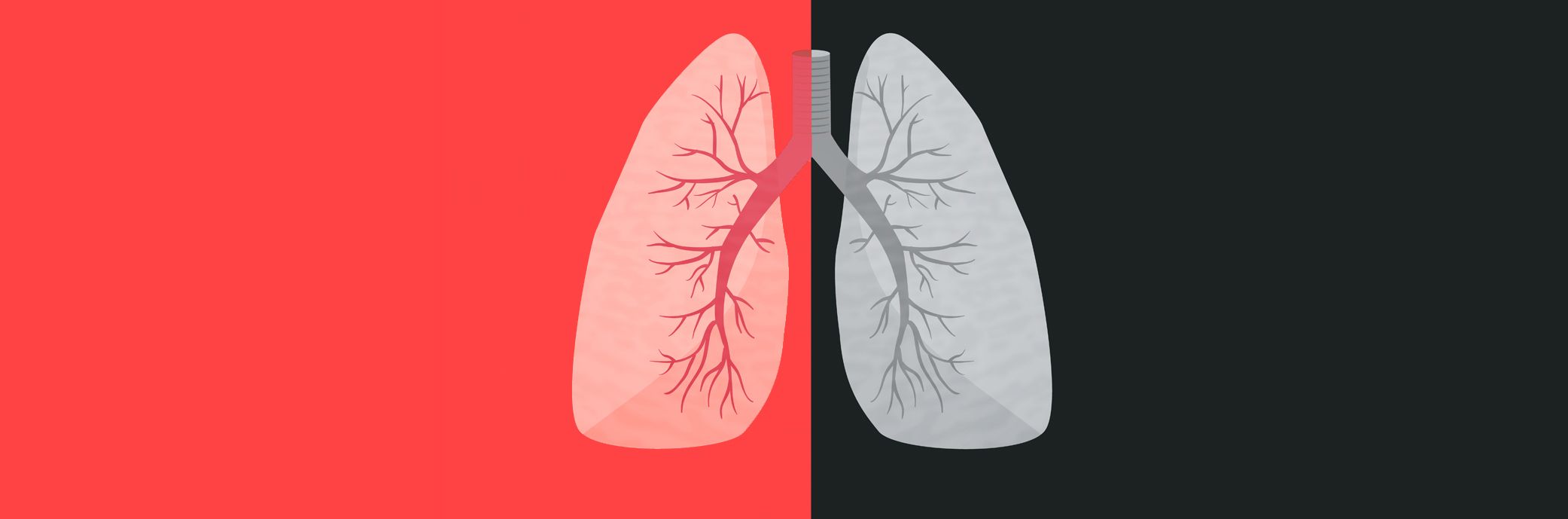
Pneumothorax occurs when air, normal circulating inside the lungs, leaks into the space between the lungs and the chest wall.
Without kewood
Diseases
Collapse light
The oxygen-enriched air, which we breathe, circulates in the lungs along an extensive network, called a bronchial tree. Hence the oxygen enters the bloodstream and heads to the heart, as well as to various organs and tissues of the body.
The collapse of the lung (pneumothorax) occurs when the air, normal circulating inside the lungs, seeps into the space between the lungs and the chest wall, pushing the lungs or causing them to appease. This leads to the fact that the affected segment of the lung turns off from work. In most cases, only one piece of lung is collaborated, the rest of the organ remains intact.
Heavy collapse can lead to a decrease in blood oxygen level, to respiratory failure, to a heart stop and shock. This is an urgent medical condition, which, with a non-time-started treatment, can lead to a fatal outcome.
Highlight two main types of pneumothorax is: traumatic pneumothorax and not traumatic pneumothorax. Any of these types can lead to a strained pneumothorax, if in the air surrounding the lungs, pressure increases. Stressful pneumothorax is often found in injuries and requires emergency medical care.
Frequent causes of traumatic type:
- fracture of the rib;
- gunshot wound;
- knife wound;
- Strong punch in the chest;
- SLR (cardiovary and pulmonary resuscitation);
- Lung biopsy (introduction of the needle through the chest wall);
- Endoscopic procedures.
In case of damage to the pulmonary fabric, it becomes less strong than healthy, therefore collaborates easier. This damage may be the result of inflammation or traumatic lung damage. However, in some cases, damage may be non-immoral genesis.
This type of pneumothorax does not occur after injury. On the contrary, it occurs spontaneously, so it is also called spontaneous pneumothorax.
There are two main types of spontaneous pneumothorax: primary and secondary. The primary spontaneous pneumothorax arises in people who have previously identified lung diseases, most often occurs in high and thin young men. Secondary spontaneous pneumothorax usually occurs in the elderly with already diagnosed lung diseases.
Frequent causes of not traumatic type are associated with:
- tuberculosis;
- pneumonia;
- lung cancer; ;
- фиброзом легких;
- муковисцидозом;
Это небольшие наполненные воздухом пузырьки, которые формируются на наружной поверхности легких. Они не являются признаком какого-либо заболевания или состояния легких, и эксперты не имеют четкого мнения, почему они формируются у некоторых людей.Sometimes these air bubbles burst spontaneously or due to a change in pressure, causing a pneumothorax.
When pneumothorax occurs for the first time, there is a sharp pain in the chest, aggravated by coughing. Difficulty breathing or shortness of breath may also be noted. For some patients, these symptoms may cause only mild discomfort and are often confused with a cold or bronchitis.
If a large portion of the lung collapses, other signs may be present along with chest pain and shortness of breath. These include:
- fast fatiguability;
- heart palpitations;
- feeling of heaviness in the chest;
- cyanotic skin tone;
- low blood pressure;
- flaring of the nostrils when breathing.
All manifestations of pneumothorax require urgent treatment. Even if symptoms of moderate severity are observed, it is necessary to seek help as soon as possible.
Diagnosis is based on the presence of air in the space around the lungs. A stethoscope can pick up changes in lung sounds, with a collapsed lung making it difficult to hear the breath sounds of the damaged lung. But detecting a small pneumothorax can be difficult. A doctor can easily identify a collapsed lung on a chest X-ray. The same is often used ultrasound. However, computed tomography of the chest organs has the greatest diagnostic value.
Radiological features
Pneumothorax is usually easily diagnosed on a chest x-ray. Typical signs:
- the visible visceral edge of the pleura looks like a very thin sharp white line;
- lung tissue is not visible on the periphery of this line;
- the peripheral space is radiolucent compared to the second lung;
- the lung may not be fully visualized;
- the mediastinum should not be displaced by a pneumothorax unless a tension pneumothorax is present;
- subcutaneous emphysema and pneumomediastinum may also be visualized;
Methods for assessing the volume of pneumothorax in percent on radiographs in direct projection include:
- % = 4.2 + 4.7 (A + B + C)
- A – maximum apical interpleural distance
- B – interpleural distance at the midpoint of the upper half of the lung
- C – interpleural distance at the midpoint of the lower half of the lung.
- % pneumothorax = 100−(DL 3/DH 3 ×100)
- DL – collapsed lung diameter
- DH is the diameter of the hemithorax on the side of the collapse
In cases where a pneumothorax is not clearly seen on a standard frontal chest x-ray, a lateral view x-ray or CT can be used.
CT scan
For the diagnosis of small pneumothoraxes, CT is more reliable than radiography. However, the method is used only in certain cases to answer specific questions.CT can be useful for determining the main reason.
Ultrasound
M-mode can be used to determine the movement of the lung in the intercostal space.
Little pneumothoraxes are best estimated in front of lying on the back (gas rises), while large pneumothoraxes are rated laterally in the middle line.
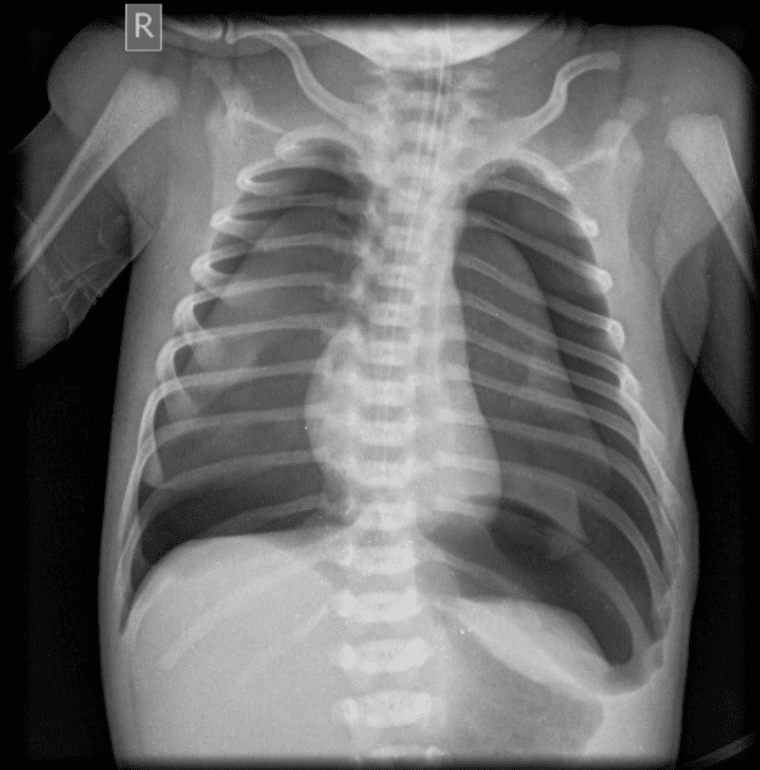
Bilateral neonatal pneumothorax
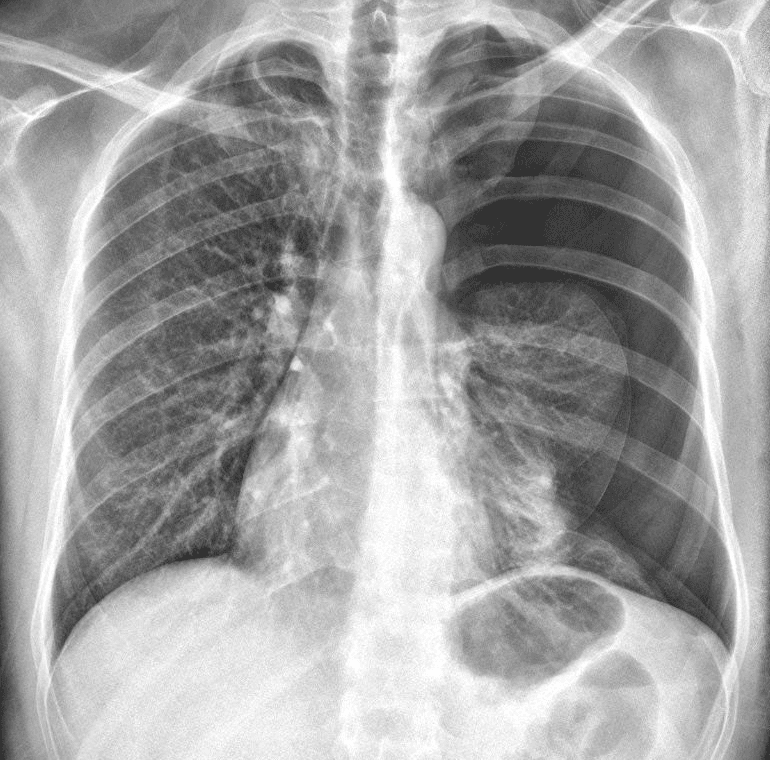
Left pneumothorax with a partial collapse of the left lung.
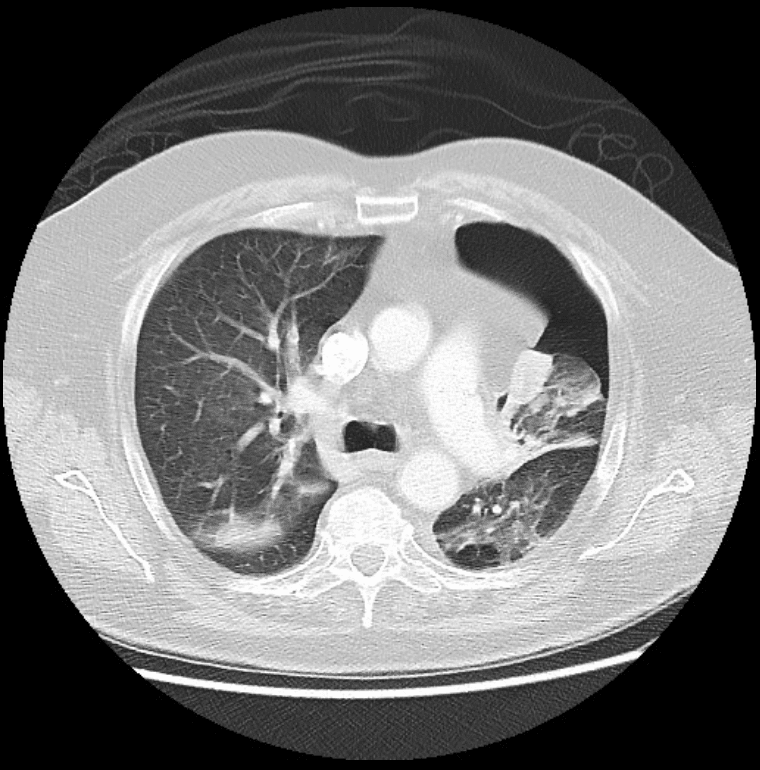
Left-sided pneumothorax associated with a partial collapse of the left upper lobe.
Collapse treatment is usually aimed at restoring the function of lung by eliminating external pressure on it. Treatment will depend on the severity of the state. Also important factor was the patient previously the pneumothorax and which symptoms are available. Available both surgical and non-surgical treatments.
In what cases does not need treatment? If the collapse is insignificant or involved only a small part of the lung, the doctor can choose the tactics of careful observation. During this period, several radiographic studies will be required. To speed up the recovery process, it will be necessary to rest more. If necessary, additional oxygen can be appointed to help you easily recover.
Removal of excess air.
With a collapse that exciting the large area of the lung, treatment is necessary to remove excess air from the chest. This process is carried out using a drainage tube or a syringe. The needle is introduced into the chest area, in the cavity near the collapse. Then the piston of the syringe on the needle is delayed, and thus pumped up air. The drainage tube is used on the same principle. However, it is usually attached to a container with a water shutter or a machine that constantly sucks the air. If the area of collaborate lung has a large area, the air can pump several days.
Operational treatment.
If the air is seeping out of the lungs and is the cause of the collapse, the surgeon needs to restore the place of flow. The doctor will make two small cuts on the chest and in one of them introduces a fiber-optic chamber to see the lung. A surgical tool is introduced into another incision, which is used to close the air flow site.
If the cause is an air bull, the surgeon has its own to close it. If the Bulla is not determined, the doctor will introduce a substance in the pleural cavity similar to Talc to cause inflammation. As a result, the pleura sheets will connect and close air leakage.
The outcome of the pneumothorax depends on the degree and type of pneumothorax. With timely provided medical care for further complications of the pneumothorax may not arise. However, if the collapse is caused by the injury, this state may repeat.According to the medicine manual, released by the Pharmaceutical Company "Merk", while eliminating the place of emergence of air from the lungs using Talc Recurble is observed in 25% of cases. With the surgical closure of the air conditioning place, recurrence is possible in 5% of cases.