Consultative and diagnostic center with a polyclinic
Atrial fibrillation (atrial fibrillation)
Patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation usually complain of bouts of irregular heartbeat. They can occur against the background of physical or emotional stress, but sometimes – on the contrary, at rest, in the evening or at night, after eating or drinking alcohol. The frequency of seizures can vary from one per year to many per day, and their duration – from a few seconds to many days and even months.
In addition, atrial fibrillation may be asymptomatic. As with all other arrhythmias, with this it is important to establish its cause, that is, to determine the underlying disease. It can be hypertension, coronary heart disease, chronic heart failure, other heart diseases (and not only the heart!).
However, there may not be any obvious cause of atrial fibrillation: then it is called idiopathic. But in any case, if the patient is diagnosed with Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation, he should know some very unpleasant things about his disease.
- It is foolish to count on the fact that atrial fibrillation, if it has appeared, will somehow resolve itself. Attacks will necessarily be repeated with a probability of 99 percent, no less.
- These attacks occur rarely at first, but gradually become more and more frequent and prolonged. In addition, more and more efforts are required to restore sinus rhythm. Sooner or later, paroxysmal atrial fibrillation becomes chronic.
- They don't die from atrial fibrillation. But you can die from its complications. The most formidable and most common complications of atrial fibrillation are called thromboembolic (blockage of an artery by a thrombus), and of these, in turn, ischemic stroke is the most common. The risk of such a stroke with atrial fibrillation increases by about 5 times. There is a special scale by which the risk of thromboembolism is calculated and medications called anticoagulants are prescribed.
To prevent attacks of atrial fibrillation, antiarrhythmic drugs are prescribed. Their choice depends on the nature of the underlying disease and many other circumstances that the cardiologist must take into account. In addition, surgical (interventional) treatment of atrial fibrillation is also possible. The task of the cardiologist-arrhythmologist is to determine the indications for the operation, prepare the patient for it and observe him after the intervention in order to help avoid possible complications.
Patients with chronic atrial fibrillation also require the attention of a cardiologist-arrhythmologist. With this form of atrial fibrillation, the most important task is the prevention of thromboembolism.Fibrillyatsiya_predserdiy_(mertsatelnaya_aritmiya)
Atrial fibrillation (atrial fibrillation)
Consultative and diagnostic center with a polyclinic 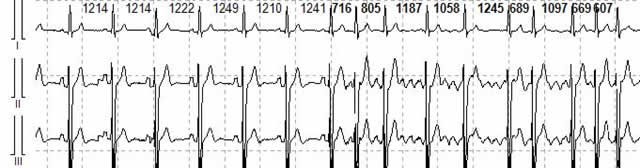
Atrial fibrillation (atrial fibrillation)
Patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation usually complain of bouts of irregular heartbeat. They can occur against the background of physical or emotional stress, but sometimes – on the contrary, at rest, in the evening or at night, after eating or drinking alcohol. The frequency of seizures can vary from one per year to many per day, and their duration – from a few seconds to many days and even months.







In addition, atrial fibrillation may be asymptomatic. As with all other arrhythmias, with this it is important to establish its cause, that is, to determine the underlying disease. It can be hypertension, coronary heart disease, chronic heart failure, other heart diseases (and not only the heart!).
However, there may not be any obvious cause of atrial fibrillation: then it is called idiopathic. But in any case, if the patient is diagnosed with Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation, he should know some very unpleasant things about his disease.
