Keeping your eyes healthy throughout your life is a rather difficult task, because today ophthalmologists have more than a hundred different eye diseases. Therefore, it is so important to visit a doctor regularly and if any alarming signs occur,
eye diseases
What are eye diseases? By what signs can they be recognized?
Keeping your eyes healthy throughout your life is a rather difficult task, because today ophthalmologists have more than a hundred different eye diseases. Therefore, it is so important to visit a doctor regularly and, if any alarming signs occur, immediately seek qualified medical help.
Know the enemy in person: eye diseases
Amblyopia
Decrease in visual acuity of one eye in the absence of pathological changes in the organ of vision.
Causes of amblyopia
- Strabismus.
- Low weight at birth.
- Cerebral palsy, developmental delay, pathologies characteristic of premature babies.
- Smoking, drinking alcohol, antibiotics during pregnancy.
- Heredity.
- Eye injury.
- Myopia, hypermetropia and other visual impairments.
- Varying visual acuity between the eyes.
Symptoms of amblyopia
- Decreased visual acuity, double vision, blurry or blurry image.
- Rapid eye fatigue, the inability to concentrate on the image for a long time.
- Involuntary movement of one eye, non-synchronous eye movements.
- Discomfort when watching TV, working with a computer or reading books, caused by the need to close the worse seeing eye.
- Overhang of the upper eyelid.
- Difficulties in determining the size of an object or the distance to it.
Treatment of amblyopia
- occlusion – closure of a poorly seeing or better seeing eye, alternately closing the eyes with an overlay;
- penalization – a temporary decrease in visual acuity of a healthy eye with the help of special drops, due to which the affected eye has to be activated;
- pleoptics and orthoptics – increased load on the diseased eye with the help of a computer program;
- surgical treatment – used when other methods are ineffective.
Anisocoria
Different pupil sizes. The norm is the difference in diameters up to 0.4 mm.
Causes of anisocoria
- Taking certain medications or drugs.
- Damage to nerve fibers, paralysis of the oculomotor nerve.
- Inflammation of the iris.
- Eye injuries, craniocerebral injuries, ophthalmic operations.
- Various pathologies of the organ of vision, for example, glaucoma.
- Infections in which the pathogen enters the central nervous system.
Symptoms of anisocoria
Headaches, dizziness, severe fatigue, distortion and blurring of the image, difficulties with the perception of space.
Treatment of anisocoria
The doctor eliminates only the cause of the disease.
Astigmatism
A congenital or acquired visual impairment in which the cornea and lens are irregularly shaped, causing light rays to fail to focus properly on the retina.
Causes of astigmatism
Congenital astigmatism occurs due to hereditary predisposition or disorders that occurred during pregnancy. Acquired astigmatism is a consequence of trauma to the cornea or lens, inflammation or other pathology of the cornea, poor-quality ophthalmic surgery.
Symptoms of astigmatism
- blurring, ghosting or distortion of the image;
- decreased visual acuity, the need to constantly squint;
- headaches and dizziness;
- fatigue, constant eye strain.
Treatment of astigmatism
Astigmatism is corrected with special glasses or contact lenses. Completely get rid of the pathology allows laser correction or surgery (up to the replacement of the lens).
optic nerve atrophy
This is the destruction of the nerve fibers of the optic nerve, which entails partial or complete loss of vision.
Causes of optic nerve atrophy
- Ophthalmic diseases: glaucoma, neuritis, retinal vein thrombosis, retinal edema and angiopathy, etc.
- Diseases of the brain and central nervous system: tumors, meningitis, multiple sclerosis, TBI, etc.
- Other diseases of the body: diabetes mellitus, atherosclerosis, systemic lupus erythematosus, syphilis, tuberculosis, SARS, influenza, measles, etc.
- Heredity.
- Toxic lesions: drugs, methyl and ethyl alcohol, tobacco.
Symptoms of optic nerve atrophy
- Decreased visual acuity, not amenable to correction, up to complete blindness.
- Narrowing of the field of view, down to one small "window".
- The appearance of large dark (blind) spots without narrowing the field of view.
- Violation of color perception.
- Narrowing of the vessels in the fundus.
- Poor pupillary response to light.
Treatment of optic nerve atrophy
- Drug therapy: vasoconstrictor, anti-inflammatory and blood circulation drugs, anticoagulants, hormones, drugs that stimulate metabolism.
- Physiotherapy: electro-, magneto-, laser stimulation, electrophoresis, ultrasound treatment, oxygen therapy.
- Surgical operations: removal of formations pressing on the nerve, implantation of tissues that allow normalization of blood circulation.
Belmo

Leukoma or thorn – persistent clouding of the cornea.
Causes of walleye
Corneal damage caused by various causes: trauma, chemical burns, radiation exposure, inflammatory, viral disease, infection, including intrauterine (herpes, syphilis, tuberculosis, chlamydia, blepharitis, trachoma, barley).
Walleye symptoms
- White spot on the eye.
- Photophobia, lacrimation.
- Decreased visual acuity, nebula of the image up to complete loss of vision.
- Redness of the eye.
- Discomfort in the eye, sensation of a foreign body.
Walleye treatment
- Drug therapy: drops and ointments that promote scar resorption, preparations for rapid regeneration, metabolic acceleration, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Surgical operations: corneal transplantation.
Blepharitis
Inflammation of the edges of the eyelids, usually occurs in a chronic form.
Causes of blepharitis
Bacterial and viral infections of both the whole organism and the organ of vision (fungal pathogens, staphylococcus aureus, herpes, intestinal bacteria, refractive errors, dry eye syndrome, intoxication, caries, sinusitis, etc.). In this case, it is necessary that the body has conditions for the growth of bacteria, for example, skin diseases or dysfunction of the glands of the eyelid.
Symptoms of blepharitis
- Change in eyelid appearance: peeling, redness, swelling.
- Discomfort in the area of the eyelid or eye.
- Photophobia.
- Image blur.
- Formation of foamy discharge and pus in the corners of the eyes.
- Crusts at the base of the eyelashes, their loss.
- Dry eyes or excessive watering.
The symptoms are more pronounced in the morning.
Treatment of blepharitis
- Compresses: help clear the excretory ducts.
- Drops and ointments: antiviral, antihistamine, antifungal, antibacterial, antiparasitic or moisturizing (for dry eye syndrome).
- Tablets: for example, tetracycline. They are prescribed if other methods are ineffective.
- Hygiene of the eyelids.
Blepharoptosis
The drooping of the upper eyelid is a violation of the muscles that raise and lower the upper eyelid.
Causes of blepharoptosis
- Absence or insufficient development of muscles.
- Damage to the optic nerve.
- Diseases of the central nervous system or brain.
- Trauma, tumor.
- Age-related muscle strain.
- Endocrine disorders, diabetes mellitus.
- Paresis, paralysis.
Symptoms of blepharoptosis
- Omission of the eyelid, narrowing of the palpebral fissure.
- Eye fatigue, double vision.
- Dry eye syndrome caused by the inability to blink.
- Discomfort associated with the development of inflammatory processes under the lowered eyelid.
- Strabismus.
- Decreased visual acuity.
Treatment of blepharoptosis
- Medication: taking vitamins, neuroprotectors, etc.
- Injections of drugs used by cosmetologists (with mild degrees): Dysport, Botulinum toxin, Lantox.
- Physiotherapy: UHF, electrophoresis, darsonvalization, massage, etc.
- Hesse or Mote operation: in the first case, the skin of the upper eyelid is sutured to the frontal muscle, and in the second, a tongue-shaped flap is cut out from the upper rectus muscle, which is sutured to the cartilage.
age-related macular degeneration
This is a progressive lesion of the central zone (macula) of the retina. It is the main cause of vision loss in old age. There are wet and dry forms.
Causes of age-related macular degeneration
- Aging of the body: dehydration, slowing down of physical reactions, metabolism, vitamin deficiency, insufficient supply of nutrients to the retina.
- Heredity.
- Smoking.
- Excessive exposure to sunlight.
Symptoms of age-related macular degeneration
- Decreased visual acuity while maintaining peripheral vision. Blurring, vagueness, distortion of straight lines, small details, etc.
- The presence of a spot in the center of the field of view.
- Inability to recognize faces.
Treatment of age-related macular degeneration
Treatment is aimed at stopping the growth of new blood vessels:
- drug therapy;
- laser coagulation of the retina;
- photodynamic therapy;
- intraocular injections;
- photocoagulation.


Hemophthalmos
Hemorrhage into the vitreous body and surrounding structures.
Causes of hemophthalmos
The main reason is a vascular defect, which happens with diabetes mellitus, post-thrombotic retinopathy, tumors, dystrophy of the center of the retina. Other reasons:
- eye diseases: glaucoma, macular degeneration, retinal detachment, developmental disorders of the eye vessels;
- diseases of the body: autoimmune diseases, a sharp increase in pressure, diseases of the circulatory system;
- eye injuries, poor-quality operations, severe shaking (for babies).
Symptoms of hemophthalmia
In addition to the aesthetic defect, they note: blurred vision, photophobia, "flies" before the eyes and symptoms of concomitant diseases.
Treatment of hemophthalmia
The main goal is to identify the cause of the hemorrhage. In most cases, the patient needs urgent hospitalization with bed rest without visual stress (reading, writing).
Of the surgical methods, laser coagulation is used, and in a more severe form, vitrectomy (removal of the vitreous body).
Hypermetropia
Visual impairment, better known as farsightedness.
Causes of hypermetropia
- Congenital: abnormal development of the eyeball, heredity, albinism, corneal pathology.
- Acquired: eye injuries, tumors, illiterate surgery, infection.
Symptoms of hypermetropia
- Inability to see nearby objects clearly.
- Pain and discomfort in the eyes, especially when working with small objects.
- Rapid eye fatigue.
- Excessive tearing.
- Photophobia.
- Headaches.
Treatment of hypermetropia
- Vision correction with glasses or contact lenses.
- Medical treatment.
- Physiotherapy.
- Visual exercises, reducing visual stress, creating optimal conditions for work (distance to the table, lack of glare, etc.).
- Operations: laser vision correction, lens replacement.
Glaucoma
An irreversible disease associated with an increase in intraocular pressure, which leads to damage to the optic nerve and blindness.
Causes of glaucoma
Increased intraocular pressure, chronic diseases of the internal organs, myopia, heredity, inflammatory eye diseases, tumors, burns and eye injuries.
Symptoms of glaucoma
Visual impairment: iridescent circles around the world, deterioration of the peripheral field of vision, “sparks” in the eyes, blurry image, night blindness, photophobia. Eye pain, nausea, and headache are also possible.
Glaucoma treatment
The main task is to reduce intraocular pressure. This is done with eye drops, tablets and injections.If these methods are ineffective, the patient makes an operation (usually the surgeon increases the outflow of intraocular fluid).
Dacryocystitis

Acquired or congenital infectious inflammation of the lacrimal bag.
Causes of dacryocystitis
The main reason is the impassability of the lacrimal channel. With congenital pathology, it arises due to the improper structure of the tear paths, the presence of the membrane or the plug. Acquired dacryocystitis arises due to tissue edema, the cause of which can be ORVI, rhinitis, nose injury or century, sinusit, etc.
Symptoms of dacryocystitis
- Painful sensations in the field of century or eyes.
- Redness, edema of the century.
- Abscess, purulent discharge instead of tears.
- Tear.
- Increased temperature, weakness.
Treatment of dacryocystitis
- Medical therapy: antibacterial, immunostimulating tablets or ointments.
- Physiotherapy: Warming up, UHF therapy, massage.
- Operations: Opening and washing of abscess, formation of a nasal canal.
- Refusal of contact lenses.
Daltonism
Congenital or acquired anomaly of color perception.
Causes of Daltonism
- Heredity.
- Injury.
- Pathology of the organs of vision (cataract, etc.) and CNS (Parkinson's disease, etc.).
- Other diseases: stroke, oncological diseases, etc.
Symptoms of daltonism
Partial (from one color) or complete inability to distinguish colors. Sometimes – light-free, tearing, pain in the eyes, twitching the eye.
Treatment of Daltonism
The disease is not treated, but the doctor can eliminate his cause.
Destruction of a vitreous body
The disease accompanied by a complete or partial change in the chemical composition, the structure and density of the gel-like substance of the vitreous body, a better known entitled "Flies in front of the eyes".
The reasons for the destruction of the vitreous body
- Ophthalmological diseases: myopia, inflammatory processes, violation of blood supply and metabolism, injury, overwork, etc.
- Other diseases of the body: diabetes, avitaminosis, stress, pathology of internal organs, atherosclerosis, hormonal failure.
Symptoms of the destruction of the vitreous body
Flies and stains before your eyes.
Treatment of the destruction of a vitreous body
- Medical treatment.
- Massage, gymnastics for eyes.
- Surgical treatment: Laser cleavage with a laser or a vitreous body removal.
Dystrophy retina
Hereditary or acquired disease characterized by violation of the visual function of the eye.
Causes of dystrophy retina
- Age changes in the body.
- The injuries of the visual body.
- Ophthalmological diseases: Cataract, myopia.
- Defeat vessels.
- Diabetes.
- Unhealthy Lifestyle.
- Heredity.
Symptoms of dystrophy retina
- Narrowing of the field of view, blind spot.
- Chicken blindness.
- Reducing visual acuity.
- Distorted forms of items.
- Sparks, dots, spots before the eyes.
- Blurred image.
Treatment of retinal dystrophy
- Drug therapy: vitamins, antioxidants, vasodilator drops, decongestants.
- Physiotherapy: phono- and electrophoresis, ultrasound treatment.
- Surgical operations depending on the type of pathology.
Cataract
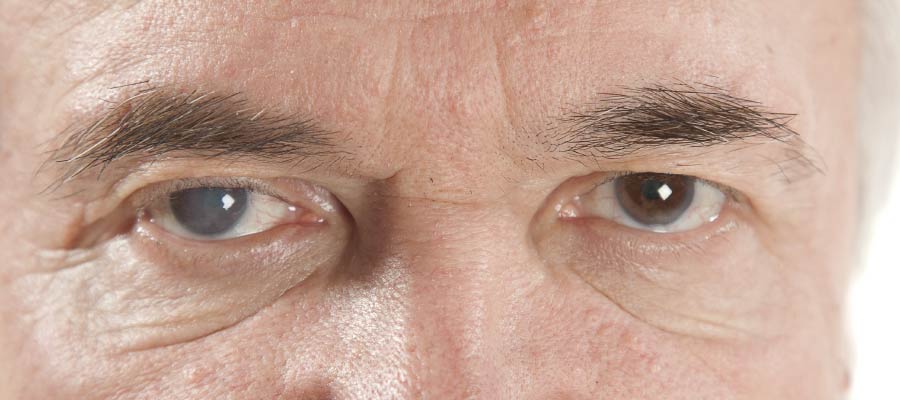
Progressive clouding of the lens. Read more in the article "Cataract".
Causes of cataract
- Age changes.
- Eye injury.
- Radiation exposure.
- Congenital pathologies.
- Concomitant pathologies: metabolic disorders, diabetes mellitus, vitamin deficiency, ophthalmic diseases.
- External factors: smoking, alcoholism, poor ecology, exposure to ultraviolet radiation.
Symptoms of a cataract
- Progressive decrease in visual acuity, change in color perception, doubling of the image.
- Light sensitivity, night blindness.
- The appearance of glare and circles before the eyes when looking at the light.
- Pupil color change.
Cataract treatment
- Drug therapy: drops and vitamins slow down the course of the disease.
- Operation: replacement of the affected lens with an artificial one.
Keratitis
Causes of keratitis
- Viruses.
- bacteria.
- Eye injury.
- Allergy.
- Avitaminosis.
- Incorrect wearing of contact lenses.
Symptoms of keratitis
- Redness of the mucous membrane of the eyelid or eye.
- Lachrymation.
- Discomfort, sensation of a foreign object in the eye.
- Convulsive contraction of the eyelids.
- Photophobia.
- Decreased visual acuity.
Antibacterial, antifungal or antiviral drops, ointments, tablets or injections.
Keratoconus

Thinning of the cornea with a subsequent change in its shape (a cone instead of a sphere).
Causes of Keratoconus
The causes of the disease have not been studied, but infections, corneal injuries, endocrine disorders, heredity, stress, poor ecology, and allergies contribute to its development.
Symptoms of keratoconus
- A sharp decrease in visual acuity, including blurry images, curved contours of objects, halos around light sources.
- Photophobia.
- Rapid eye fatigue.
Treatment of keratoconus
- Vision correction with cylindrical glasses and hard contact lenses.
- Operations: keratoplasty (corneal transplantation), correction of the cornea shape with a laser, implantation of stromal rings (introduction of additional elements into the cornea).
- Crosslinking: impact on the cornea with drops and a special device.
computer vision syndrome
A complex of symptoms that occur when working at a computer.
Causes of computer vision syndrome
- Constant eye strain.
- Incorrect ergonomics of the workplace, lighting, brightness and height of the display, distance to the monitor.
- Emission from the monitor and incorrect color setting.
- Dusty room.
Symptoms of computer vision syndrome
- Dry eye syndrome.
- Sensation of a foreign object in the eye.
- Headache.
- Fast fatigue eye.
- Reducing visual acuity.
- Difficult focusing on close objects after distant and vice versa.
- Photophobia.
- Redness eye.
- Tear.
Treatment of computer visual syndrome
It is necessary to properly equip the workplace, use drops of type "artificial tear", check the visual sharpness and buy glasses for a computer.
Conjunctivitis
Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eyelid and the white part of the eyeball.
Causes of conjunctivitis
- Bacteria: chlamydia, staphylococci, streptococci, etc.
- Viruses: adenovirus, herpes.
- Fungi: Candids, Aspergilla, etc.
- Allergies, stimuli (caustic smoke, etc.).
Symptoms of conjunctivitis
- Edema and redness of both century.
- Pump, eyelid stick after sleep.
- Discomfort in the eye, feeling of the foreign object.
- Photophobia.
- Tear.
- Involuntary blink.
- Dry eye syndrome.
Treatment of conjunctivitis
Antibacterial, antiviral, antifungal or anti-allergic ointments, drops, tablets, means for local immunity, type "artificial tear".
Strabismus

Permanent or periodic deviation of one or two eyes when looking straight.
Causes of space
- Congenital: heredity, mother's disease, smoking, alcohol use during pregnancy, premature genera, low body weight during childbirth.
- Acquired: diseases of the eyes, infection, stress, fright, load on the organ of view, the pathologies of the eye muscles, tumors, encephalitis, multiple sclerosis.
Cultural treatment
- Eye patch.
- Wearing glasses or contact lenses.
- Electrostimulation, laser therapy, ambocution.
- Surgical operations restoring the location of the eyeballs.
Myopia
Violation of vision, more famous called "Myopia".
Causes of myopia
Congenital myopia is a consequence of amblyopia and anomalies of eye development. The acquired occurs due to large loads on the eyes, including the growth of the eyeball. The likelihood of myopia is higher under adverse heredity, increased intraocular pressure.
Symptoms of myopia
- Reducing visual acuity – a person does not see the remote objects.
- Discomfort in the eyes, thread, pain, fast fatigue.
- Headaches in the forehead, temples.
Treatment of myopia
- Optical correction. Patients prescribe contact lenses or glasses.
- Medical treatment. Preparations for relaxing eye muscles, improving the state of the retina, polyvitamins, etc.
- Surgical operations. With the help of a laser or other methods, change the shape of the cornea.
Neurry optic nerve
Inflammation of the optic nerve.

Causes of neuritis
- Inflammatory brain diseases.
- Ophthalmological diseases.
- Diseases of other parts of the body: throat, ears, nose, teeth.
- Infections.
- Intoxication.
Symptoms of neuritis
- Reducing visual acuity, blurred image, including hoppy.
- Distortion of color perception.
- Narrowing of the field of vision, the appearance of a "blind spot".
- General malaise: high fever, cough, runny nose, headache, vomiting, palpitations, dermatitis, fatigue, etc.
- Photophobia.
- Chicken blindness.
- Pain in the eyes, especially when moving.
- Flies, dots, flashes before the eyes.
Treatment of neuritis
The doctor treats the disease that provoked neuritis. The pathology itself is treated with corticosteroids, antibiotics, vitamins, antiviral and antihistamines. Physiotherapy is rarely prescribed: magneto-, electro-, reflex- and laser therapy, ultrasound treatment.
Nervous tic
Prolonged (up to several days) twitching of the eye. Read more in the article "Why the eye twitches."
Causes of a nervous tic
- Stress, overwork, excitation of the central nervous system.
- Lack of sleep.
- Abuse of alcohol, energy drinks, coffee.
- Work in poor lighting.
- Lack of vitamins.
- neurological diseases.
Symptoms of a nervous tic
- Eye twitching.
- Itching, pain and other discomfort in the eyes.
Nervous tic treatment
Elimination of the cause that caused the tick: rest, strengthening the immune system, proper nutrition, taking sedatives, caring for vision, gymnastics for the eyes.
Optical neuropathy
Damage to the fibers of the optic nerve.
Causes of optic neuropathy
- Circulatory disorders of the optic nerve.
- Cardiovascular diseases.
- Inflammation of the optic nerve.
- Tumors.
- Eye trauma, traumatic brain injury.
- Lack of vitamins, depletion of the body.
- Heredity.
- Intoxication.
- Ophthalmic diseases, in particular glaucoma.
Symptoms of optic neuropathy
- Violation of color perception.
- Rapid decrease in visual acuity.
- Narrowing of the field of view.
- Pain, pressure in the eyeballs.
- Involuntary eye movements.
- Dizziness, nausea, vomiting, headache.
Treatment of optic neuropathy
Medicines that dilate blood vessels, reduce swelling and restore blood clotting, vitamin complexes. Therapy, together with the ophthalmologist, is selected by the therapist, neurologist and cardiologist.
Edema of the eyelids
Excessive accumulation of fluid in the eyelids. Read more in the article "Swelling of the eyes".
Causes of swelling of the eyelids
- Ophthalmic diseases: conjunctivitis, brefaritis, barley, keratitis, etc.
- Diseases of the body: trauma, allergies, dermatitis, vegetovascular dystonia, hormonal failure, kidney disease, etc.
- Other causes: alcohol consumption, lack of sleep, exposure to ultraviolet radiation, tattooing, insect bites, etc.
Eyelid swelling symptoms
- Redness or pallor of the skin.
- Feeling of tightness in the skin.
- Swelling of the eyelid.
- Narrowing of the palpebral fissure.
- Discomfort in the eye area.
Eyelid swelling treatment
- Drug therapy, the use of cosmetics (masks, etc.).
- Lymphatic drainage massage.
- Physiotherapy: electrical and myostimulation, fractional thermolysis, cryotherapy.
- Mesotherapy.
- Gymnastics for the eyes.
- Surgical treatment – lifting and removal of excess adipose tissue.
Retinal disinsertion
Separation of the inner layers of the retina from the epithelium and choroid.
Causes of retinal detachment
- High degree of myopia.
- Dystrophic changes in the retina.
- Injuries, physical stress.
- Diabetes.
Retinal detachment symptoms
- Lightning and sparks in the eyes.
- Decreased visual acuity.
- Veil before the eyes.
- Restriction of the field of view.
- Distorted perception of the shape and size of objects.
Retinal detachment treatment
Urgent surgical treatment – the doctor closes the gap with a filling or laser photocoagulation.
Ophthalmic rosacea
Chronic reddening of the skin with a transition to the eyes.
Causes of ophthalmic rosacea
Violation of vascular regulation. Risk factors: smoking, alcohol consumption, exposure to UV rays, cold air, temperature changes, gastrointestinal diseases, unhealthy diet.
Symptoms of ophthalmic rosacea
- Dryness and irritation of the eyes.
- Decreased visual acuity.
- Redness of the eyes.
- Itching, burning and other discomfort.
- Puffiness of the eyelids.
- Loss of eyelashes.
- Dandruff and greasy scales on eyelashes and eyelids.
- Photophobia.
- Blepharitis.
Treatment of ophthalmic rosacea
- Eye hygiene.
- The use of anti-inflammatory, antibacterial drops and ointments, drops of the "artificial tear" type.
- Warm compresses, washing with Furacilin.
- Eyelid massage.
pterygium
Growth of the conjunctiva from the corner of the eye to the center of the cornea.
Causes of pterygium
UV exposure. Risk factors: dry eye syndrome, working at a computer, in a dusty room, poor environment, inflammatory eye diseases.
Symptoms of pterygium
- Triangular spot on the cornea.
- Redness of the eye.
- Discomfort: sensation of a foreign object, itching, burning.
- Mucosal edema.
- Decreased visual acuity, feeling of a veil before the eyes.
Treatment of pterygium
- Drug treatment: corticosteroids, artificial tear drops.
- Surgical treatment: removal of the defect.
Presbyopia

Age-related decrease in visual acuity near – age-related farsightedness.
Causes of Presbyopia
Loss of lens elasticity and ability to change curvature with age (usually after 60 years).
Symptoms of presbyopia
- Inability to see nearby objects clearly.
- Eye fatigue.
- Headaches.
- General fatigue.
Presbyopia treatment
- Vision correction with conventional or progressive glasses or multifocal contact lenses, monocular vision correction.
- Surgical treatment: replacement of the lens with an intraocular lens.
Retinitis
Causes of retinitis
- Bacteria and viruses.
- Injuries, poorly performed operations on the eyes.
- Exposure to sunlight.
- Intoxication.
- Allergy.
Retinitis symptoms
- Decreased visual acuity, the formation of "blind spots".
- Flickering images, sparks before the eyes.
- Double vision.
- Chicken blindness.
- Change in color perception.
- Distorted perception of the shape of objects.
Retinitis treatment
The use of antibiotics and antiviral drugs: locally, in the form of injections is less frequently orally. In case of hemorrhages, the vitreous body is removed, the retina closes the tip.
Dry Eyes Syndrome
Violation of the process of products and outflows of tears.
Causes of dry eye syndrome
Insufficient tear formation. Risk Factors: SHEGREEN Syndrome, Elderly Age, Eye Burns, Acceptance of Medicines, Work In Adverse Conditions (Dry, Cold Air, Computer Work), Chronic Inflammatory Eye Diseases, Endocrine Diseases.
Symptoms of dry eye syndrome
- Dryness or on the contrary, tearing.
- Discomfort in the eyes: burning, thread, feeling of the foreign body, sand in the eyes.
- Redness eye.
- Photophobia.
- Feeling pressure in the eyes.
- Stunning eyelid.
Treatment of dry eye syndrome
- Drops of type "Artificial tear".
- Anti-inflammatory medicines.
Trachoma
Infection affecting conjunctiva and cornea.
Causes of trachomas
Symptoms of trachomas
- Redness or white type of conjunctiva.
- Treatment of the eyes.
- Streetness of the eyelids.
- Purulent discharge.
- Discomfort in the eye area.
- Scars on conjunctive.
- Whole sensitivity.
- Ptosis of the century.
- The formation of the capsules around the follicle, follicle folling.
Treatment of trachomas
- Medical therapy: antibacterial solutions, drops, ointments, vitamin complexes, immunomodulators, antibiotics (in injections), antimicrobial means.
- Surgical methods: Opening of follicles, plastic of the affected century.
- Refusal to carry contact lenses.
Uveite
Inflammation of the vascular shell of the eye, sometimes together with the surrounding tissues.
Causes of Uveita
- Heredity.
- Infection: bacteria or viruses.
- Autoimmune diseases.
- Eye injuries.
Symptoms of Uveita
- Photophobia.
- Reducing visual acuity, blurred, foggy image.
- Redness eye.
- Pain in the eye.
- Tear.
- Changing pupils, iris colors.
- Spots, flies, flashes before your eyes.
- Increase intraocular pressure.
Treatment of Uveita
- Medical therapy: Midships (drops for the expansion of pupils), hormonal, anti-inflammatory (locally and intravenous), antibacterial, antiviral, antihistamines.
- Physiotherapy.
- Surgical separation of adhesions.
Photophobia

The disease, a better known called "Svetoboyazn". Read more in the article "Svetoboyazn".
Causes of photophobia
- Congenital features of the eyes.
- Receive medicines.
- Long work at the computer.
- Work in adverse conditions: dry, dusty, dark room.
- Long-term eye stress.
- Ophthalmological diseases: keratitis, conjunctivitis, etc.
- CNS diseases and other pathologies.
Symptoms of photophobia
- The intolerance of even a laundry light for a long time, the desire to pushed.
- Discomfort in the eyes.
- Tear.
- Increase the size of pupils.
- Redness eye.
- Reducing visual acuity.
- Spots, points, lightning in front of the eyes.
- Eye fatigue.
- Headache, dizziness.
Treatment of photofobia
- Treatment of the disease that caused photophobia.
- Wearing sunglasses, "chameleons", glasses for working at a computer.
- Drops of type "Artificial tear".
Ecropion
Disease, better known as the inverting of the lower eyelid.
Reasons for the palpitude of the lower eyelid
- Congenital formed intrauterine anomaly.
- Age reduction of muscle tone.
- Inflammatory diseases: conjunctivitis, blepharitis.
- Paralysis or paresis of facial nerve.
- Various diseases of the body: Down syndrome, systemic red lupus, dermatomyomyosis, neoplasms, etc.
Symptoms of theft of the lower eyelid
- Tear.
- Frequent blinking.
- Discomfort, burning, the feeling of sand in the eyes.
- Expansion of vessels in the eye.
- The inability to completely close the eyes.
- Keratitis and other inflammatory diseases.
Treatment of theft of the lower eyelid
Blerofaroplasty: restoration of the anatomical structure of the century.
Electrophthalmia
Electrophthalmia, photo phthalmia or snowy blindness – inflammatory eye disease.
Causes of electrophthalmia
Bright effects of sunlight or ultraviolet: lamps for tanning, lightning, sun, photo flashlights, spotlights, welding machine, quartz lamps, glare on water, light from snow.
Symptoms of electrophthalmia
- The feeling of the foreign body in the eye.
- Discomfort in the eyes, thumb, pain, irritation.
- Inspection of the eyelid.
- Reducing visual acuity.
- Redness eye.
- Tear.
- Increase body temperature, headache.
- The edema of the cornea.
- Whole sensitivity.
Treatment of electrical phthalmia
- Wash eye with water or saline.
- Cold compresses.
- Drug therapy: ointment, drops, cell recovery tablets, with anesthetic, vasoconstrictor, healing, antibacterial effect.
Barley
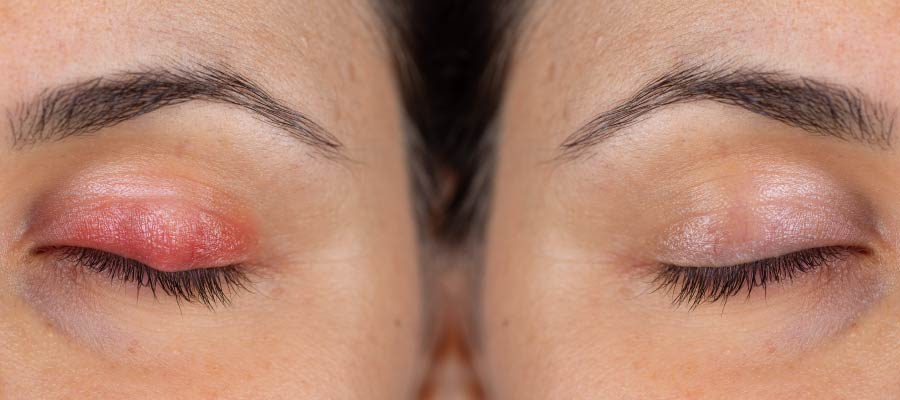
Barley (Gordeolum) – acute purulent inflammation. Read more in the article "Barley".
Causes of barley
Bacterial infection: Streptococcus, Golden Staphylococcus, God Demodex tick. Risk factors – supercooling, cold, weakened immunity, oily leather, diabetes, chronic eye disease, endocrine system, gastrointestinal tract, allergies, insufficient hygiene, poor ecology, injuries.
Symptoms of barley
- Plowing, similar to acne.
- Redness, edema of the century.
- Discomfort in the eye, itching, pain.
- Tear.
- Headache, general malaise, elevated body temperature, increase in lymph nodes.
Treatment of barley
- Warm compresses.
- Medical therapy: antibacterial and wound-healing ointments and drops that strengthen immunity drugs.
- UHF therapy.
- Surgical intervention.
To preserve the health of your eyes, we recommend contacting medical professionals at least twice a year. By the way, checking the vision and selection of contact lenses in the salons of Optics "CHALKARIK" are free for buyers.Accompanying an ophthalmologist for a year is a gift.
