Plasmapheresis plasmapheresis (from Plasma – blood plasma and apheresis – exclusion or removal) – one of the main methods of efferent therapy, which consists in mechanical removal of the blood plasma part
Plasmapheres
Plasmapheresis (from Plasma – blood plasma and apheresis – exclusion or removal) is one of the main methods of efferent therapy, which consists in mechanical removal of a part of the patient's blood plasma with a substitution of its volume with a physiological solution or solutions of blood substitutes or donor plasma.
Plasmapheresis, as a procedure, is divided into donor and therapeutic (therapeutic). Donor Plasmapheresis is carried out with the aim of plasma for the donor for subsequent use for medical purposes. Therapeutic plasmapheresis is carried out with therapeutic purposes in the treatment of various diseases, which today has more than 200.
Blood, as is known, consists of uniform elements (blood cells) – erythrocytes (red blood cells), leukocytes (white blood cells), platelets (cells involved in blood intake process), and liquid in which these cells are in suspended state . This fluid, called blood plasma, is a complex, multicomponent solution of proteins and electrolytes.
During the procedure of plasmapheresis, regardless of the method, plasma and blood cells are separated. The resulting plasma containing both harmful and useful substances is removed, and the condensed cellular cell mass is divorced by an isotonic solution of sodium chloride or another plasma refurbishment and is returned to the patient. During one session, it is removed from 500 to 900 ml of plasma, which seems sufficiently safe and can only be ashamed by crystalloid solutions. In the first hours after the plasma session, a significant decrease in the concentration of pathological products is observed. However, in response to the removal of part of the plasma, the body has an outflow of the tissue fluid into the bloodstream and the release of tissues from the toxic harmful substances there, and after a few hours, their content in the blood approaches the initial level. Subsequent sessions of plasmapheresis contribute to the removal and these substances, which leads to a more complete sanitation of the entire internal environment, given that the main part of the harmful products is in emergency spaces. In principle, this is the main task of efferent therapy – removal of autoantiboders from targets, detoxification.
After removing part of the plasma, the system of regulating the composition of the inner environment of the body immediately launches the mechanism of replenishing remote ingradients, however, the normal components are discarded mainly, which in the "refreshed" medium retain their properties. In addition, blood viscosity decreases and microcirculation improves accordingly – minor vessels are opened, which enhances the power and breathing of the cells.
The plasma obtained during the procedure is disposed of. Before returning to the bloodstream, the cell mass can also be subjected to additional processing, for example, ultraviolet irradiation, exposure to medicinal substances (hormones, antibiotics, antiallergic drugs).
The main factors that determine the therapeutic effect of plasmapheresis are:
Together with the plasma, the substances contained in it are removed, which caused or can cause the disease or aggravate its course. These are substances such as cholesterol, pathological immunoglobulins, circulating immune complexes (CIC), uric acid, toxins, end products of protein metabolism (creatinine, urea), etc.
Substitution of part of the plasma with saline and blood substitutes improves the rheological properties (fluidity) of the blood.
Removal of part of the plasma causes a response of the body, with the activation of natural defense mechanisms.
Plasmapheresis can be performed both in the hospital and on an outpatient basis. With outpatient plasmapheresis, 15-20% of the circulating plasma is removed, the circulating blood volume is restored by saline transfusion. The procedure takes 40 to 90 minutes. It is carried out from 3 to 5 sessions with an interval of 1-3 days, depending on the disease, it is possible to extend the course up to 10 procedures. Repeated courses are recommended after 6-12 months, but not earlier than after 2 months.
The use of plasmapheresis in the early stages of the disease helps to prevent irreversible organ disorders, and in the later stages to prevent crises of severe complications, increase the body's susceptibility to prescribed medications. Plasmapheresis by itself, as a rule, does not solve the problem of treating patients; it is effective with rational drug therapy. The introduction of plasmapheresis into the complex therapy of chronic diseases can quickly improve the condition of patients, reduce the duration of treatment and medication, and prolong remission. The most important factor on which the duration of the effect after the course of plasmapheresis depends is precisely the correctly selected basic drug therapy for the underlying disease.
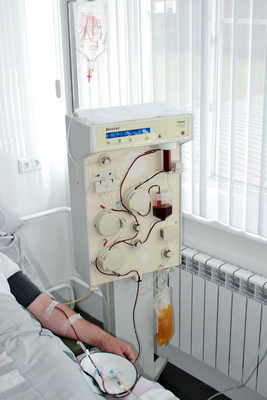
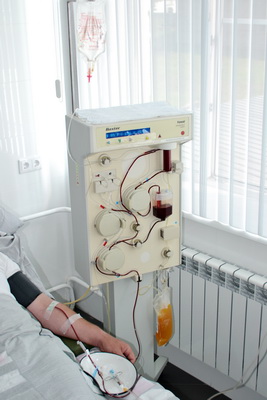
Hardware plasmapheresis
In our department, both discrete and hardware plasmapheresis are performed on the Baxter Autopheresis-C device. Device advantages:
- Works according to the sparing and safest single-needle scheme for connecting a single peripheral vein. A two-way connection is also possible.
- It has a closed single-use extracorporeal circuit that maintains tightness during the procedure, which eliminates the possibility of infection for the patient and the doctor.
- Adaptively adjusts to the patient's venous blood flow.
- You can set the optimal parameters that ensure high-quality and safe conduct of the procedure.
- Easier tolerated by patients, especially in serious condition, with unstable hemodynamics, preeclampsia in pregnant women, in old age.
Procedures are performed using American certified disposable sterile kits.
In order to undergo a course of plasmapheresis in the department of gravitational blood surgery, you must make an appointment with a transfusiologist.
Surveys
- General blood analysis
- total protein
- RW
- HIV
- Hepatitis B and C
- Blood type
Additionally, if necessary:
- Coagulogram
- General urine analysis
- ECG
Indications for plasmapheresis
1. Autoimmune diseases:
- autoimmune ophthalmoplegia;
- type I diabetes mellitus, autoimmune retinopathy in diabetes mellitus;
- autoimmune thyroiditis;
- bronchial asthma, fibrosing alveolitis, sarcoidosis;
- viral hepatitis B and C;
- rheumatoid arthritis, polyarthritis, dermatomyositis, systemic lupus erythematosus, vasculitis;
- multiple sclerosis, myasthenia gravis, Guillain-Barré syndrome;
- Raynaud's disease (endarteritis);
- autoimmune infertility.
Antibody attacks cause a constant progression of diseases, and their treatment is reduced mainly to symptomatic therapy. The "scooping out" of autoantibodies during plasmapheresis leads to a long-term improvement in the nature of the course of the disease. Autoantibodies are formed very slowly. At low concentrations, they do not have a damaging effect on the body. To do this, you need to reach a certain "threshold" value of the content in the blood. Performing 3-4 plasmapheresis procedures guarantees the absence of signs of exacerbation of the process for 1 or more years.
2. Immunity disorders:
- immunodeficiency states: frequent colds; furunculosis, herpes and other chronic bacterial and viral infections;
- in ophthalmology – recurrent keratouveitis, infectious endophthalmitis;
- chronic inflammatory diseases of the upper respiratory tract, gastrointestinal and urogenital tracts;
- various types of allergies (drug and food), hay fever, atopic dermatitis, neurodermatitis, psoriasis.
When the plasma in its composition is removed, the signals of the immune system are also removed. Moreover, those whose concentration is overestimated are removed in larger quantities. If this is a lack of immunity – signals that inhibit the immune response, if there is an excess of immunity – then, accordingly, signals that activate the immune response. Thus, the "distortion" in the state of activation and inhibition of immunity, which can be observed after the occurrence of various stressful conditions, is eliminated.
3. Diseases of "accumulation" – mainly gout and atherosclerosis in all its variety of manifestations:
- coronary artery disease;
- atherosclerosis of the vessels of the lower extremities;
- atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels, including the retina.
The removal of cholesterol in the plasma leads to the following effect: fresh cholesterol deposited on the walls of blood vessels, according to the difference in concentrations, will pass into the blood, where its concentration is sharply reduced.During the next procedure of plasmapheresis, cholesterol is again removed. It is further separated from the walls of the vessels and goes into the blood. So, for several sessions, you can clean the vessels from the layers of cholesterol recently. As of blood flow, general health and appearance, you can return a few years ago.
4. Diseases caused by hormonal disorders:
- diabetes mellitus – blood circulation is improved according to the affected vessels, sensitivity to hypoglycemic drugs is restored;
- thyrotoxicosis – the toxic effect of the thyroid hormones is removed;
Climate disorders – defective sex hormones are removed, which are formed in this period in high concentration and cause various well-being disorders; - Hypertensive disease – initial stage, the unstable form is also due to hormonal imbalance (so far the autoregulation has not "focused" blood pressure level at a new level, it is possible to return to the normal level without the use of drugs – only by removing the plasma and all the signals contained in it; , the sensitivity of the body towards hypotensive drugs increases).
5. Diseases caused by chronic or acute microcirculation disorders.
In ophthalmology, these are trophic and toxic lesions of the optic nerve, sharp thrombosis of the artery and veins of retina.
6. As a common matter, the procedure.
Abroad plasmapheresis is carried out even healthy people to extend active longevity. Extensiveness of the testimony to Plasmapheresis covers a variety of medicine areas – from the treatment of newborns before the treatment of elderly patients, from resuscitation departments to preventive outpatient procedures.